Tissue-specific small heat shock protein 20 activation is not associated with traditional autophagy markers in Ossabaw swine with cardiometabolic heart failure
- PMID: 32946285
- PMCID: PMC7789972
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00580.2020
Tissue-specific small heat shock protein 20 activation is not associated with traditional autophagy markers in Ossabaw swine with cardiometabolic heart failure
Abstract
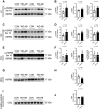
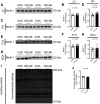
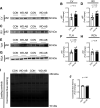
The small heat shock protein 20 (HSPB6) emerges as a potential upstream mediator of autophagy. Although autophagy is linked to several clinical disorders, how HSPB6 and autophagy are regulated in the setting of heart failure (HF) remains unknown. The goal of this study was to assess the activation of the HSPB6 and its association with other well-established autophagy markers in central and peripheral tissues from a preclinical Ossabaw swine model of cardiometabolic HF induced by Western diet and chronic cardiac pressure overload. We hypothesized HSPB6 would be activated in central and peripheral tissues, stimulating autophagy. We found that autophagy in the heart is interrupted at various stages of the process in a chamber-specific manner. Protein levels of HSPB6, Beclin 1, and p62 are increased in the right ventricle, whereas only HSPB6 was increased in the left ventricle. Unlike the heart, samples from the triceps brachii long head showed only an increase in the protein level of p62, highlighting interesting central versus peripheral differences in autophagy regulation. In the right coronary artery, total HSPB6 protein expression was decreased and associated with an increase in LC3B-II/LC3B-I ratio, demonstrating a different mechanism of autophagy dysregulation in the coronary vasculature. Thus, contrary to our hypothesis, activation of HSPB6 was differentially regulated in a tissue-specific manner and observed in parallel with variable states of autophagy markers assessed by protein levels of LC3B, p62, and Beclin 1. Our data provide insight into how the HSPB6/autophagy axis is regulated in a preclinical swine model with potential relevance to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Our study shows that the activation of HSPB6 is tissue specific and associated with variable states of downstream markers of autophagy in a unique preclinical swine model of cardiometabolic HF with potential relevance to HFpEF. These findings suggest that targeted approaches could be an important consideration regarding the development of drugs aimed at this intracellular recycling process.
Keywords: HFpEF; autophagy; coronary vasculature; heart; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The right ventricular transcriptome signature in Ossabaw swine with cardiometabolic heart failure: implications for the coronary vasculature.Physiol Genomics. 2021 Mar 1;53(3):99-115. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00093.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Physiol Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33491589 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of BECN1-mediated autophagy by HSPB6: Insights from a human HSPB6S10F mutant.Autophagy. 2018;14(1):80-97. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1392420. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29157081 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of macroautophagy and chaperone-mediated autophagy in human skeletal muscle by high-intensity exercise in normoxia and hypoxia and after recovery with or without post-exercise ischemia.Free Radic Biol Med. 2024 Sep;222:607-624. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.07.012. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39009244
-
Small heat shock protein 20 (HspB6) in cardiac hypertrophy and failure.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011 Oct;51(4):574-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Sep 30. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 20869365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The small heat shock protein, HSPB6, in muscle function and disease.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010 Jan;15(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s12192-009-0127-8. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010. PMID: 19568960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic high-rate pacing induces heart failure with preserved ejection fraction-like phenotype in Ossabaw swine.Basic Res Cardiol. 2022 Oct 12;117(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s00395-022-00958-z. Basic Res Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 36222894 Free PMC article.
-
8-Br-cGMP activates HSPB6 and increases the antineoplastic activity of quinidine in prostate cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Feb 19;10(1):90. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01853-3. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38374143 Free PMC article.
-
Tim-1 alleviates lupus nephritis-induced podocyte injury via regulating autophagy.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2021;46(3):305-313. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2021.109827. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34764802 Free PMC article.
-
A Porcine Model of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction Induced by Chronic Pressure Overload Characterized by Cardiac Fibrosis and Remodeling.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jun 2;8:677727. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.677727. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34150870 Free PMC article.
-
The right ventricular transcriptome signature in Ossabaw swine with cardiometabolic heart failure: implications for the coronary vasculature.Physiol Genomics. 2021 Mar 1;53(3):99-115. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00093.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Physiol Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33491589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chu G, Egnaczyk GF, Zhao W, Jo SH, Fan GC, Maggio JE, Xiao RP, Kranias EG. Phosphoproteome analysis of cardiomyocytes subjected to β-adrenergic stimulation: identification and characterization of a cardiac heat shock protein p20. Circ Res 94: 184–193, 2004. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000107198.90218.21. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum, 1988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I01BX003271/U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)/International
- R01 HL136292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX004016/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- HL125503/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHBLI)/International
- I01 BX004220/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- K01 AG041208/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG041208/HHS | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)/International
- R37 DK037175/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000371/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR060268/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL125503/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK097512/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL136292/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHBLI)/International
- HL112998/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHBLI)/International
- I01 BX003271/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

