A ribosomal RNA fragment with 2',3'-cyclic phosphate and GTP-binding activity acts as RIG-I ligand
- PMID: 32946572
- PMCID: PMC7544222
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa739
A ribosomal RNA fragment with 2',3'-cyclic phosphate and GTP-binding activity acts as RIG-I ligand
Abstract
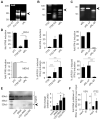
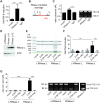
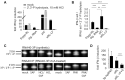
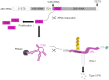
The RNA helicase RIG-I plays a key role in sensing pathogen-derived RNA. Double-stranded RNA structures bearing 5'-tri- or diphosphates are commonly referred to as activating RIG-I ligands. However, endogenous RNA fragments generated during viral infection via RNase L also activate RIG-I. Of note, RNase-digested RNA fragments bear a 5'-hydroxyl group and a 2',3'-cyclic phosphate. How endogenous RNA fragments activate RIG-I despite the lack of 5'-phosphorylation has not been elucidated. Here we describe an endogenous RIG-I ligand (eRL) that is derived from the internal transcribed spacer 2 region (ITS2) of the 45S ribosomal RNA after partial RNase A digestion in vitro, RNase A protein transfection or RNase L activation. The immunostimulatory property of the eRL is dependent on 2',3'-cyclic phosphate and its sequence is characterized by a G-quadruplex containing sequence motif mediating guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) binding. In summary, RNase generated self-RNA fragments with 2',3'-cyclic phosphate function as nucleotide-5'-triphosphate binding aptamers activating RIG-I.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



References
-
- Blasius A.L., Beutler B.. Intracellular toll-like receptors. Immunity. 2010; 32:305–315. - PubMed
-
- Yoneyama M., Kikuchi M., Natsukawa T., Shinobu N., Imaizumi T., Miyagishi M., Taira K., Akira S., Fujita T.. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004; 5:730–737. - PubMed
-
- Kato H., Takeuchi O., Sato S., Yoneyama M., Yamamoto M., Matsui K., Uematsu S., Jung A., Kawai T., Ishii K.J. et al.. Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature. 2006; 441:101–105. - PubMed
-
- Kato H., Takeuchi O., Mikamo-Satoh E., Hirai R., Kawai T., Matsushita K., Hiiragi A., Dermody T.S., Fujita T., Akira S.. Length-dependent recognition of double-stranded ribonucleic acids by retinoic acid-inducible gene-I and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5. J. Exp. Med. 2008; 205:1601–1610. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

