Streptococcus equi Subspecies zooepidemicus and Sudden Deaths in Swine, Canada
- PMID: 32946731
- PMCID: PMC7510724
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2610.191485
Streptococcus equi Subspecies zooepidemicus and Sudden Deaths in Swine, Canada
Abstract
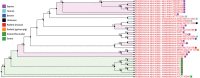
Historically described as a commensal of the swine upper respiratory tract, Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus was previously reported as an important swine pathogen only in Asia. Here we report the isolation and whole genome characterization of S. equi subsp. zooepidemicus associated with a sudden death outbreak in pigs in Canada.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Canada; Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae; Streptococcus equi; bacteria; cocci; lymph nodes; mortality; outbreak; pneumonia; sows; sudden deaths; swine; zooepidemicus.
Figures
References
-
- Feng Z, Hu J. Outbreak of swine streptococcosis in Sichan province and identification of pathogen. Anim Husbandry Vet Med Lett. 1977;2:7–12.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

