Elaeagnus angustifolia Plant Extract Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Induces Apoptosis via HER2 Inactivation and JNK Pathway in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 32947764
- PMCID: PMC7570883
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184240
Elaeagnus angustifolia Plant Extract Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Induces Apoptosis via HER2 Inactivation and JNK Pathway in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
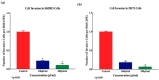
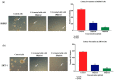
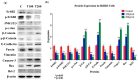
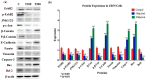
Elaeagnus angustifolia (EA) is a medicinal plant used for treating several human diseases in the Middle East. Meanwhile, the outcome of EA extract on HER2-positive breast cancer remains nascent. Thus, we herein investigated the effects of the aqueous EA extract obtained from the flowers of EA on two HER2-positive breast cancer cell lines, SKBR3 and ZR75-1. Our data revealed that EA extract inhibits cell proliferation and deregulates cell-cycle progression of these two cancer cell lines. EA extract also prevents the progression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), an important event for cancer invasion and metastasis; this is accompanied by upregulations of E-cadherin and β-catenin, in addition to downregulations of vimentin and fascin, which are major markers of EMT. Thus, EA extract causes a drastic decrease in cell invasion ability of SKBR3 and ZR75-1 cancer cells. Additionally, we found that EA extract inhibits colony formation of both cell lines in comparison with their matched control. The molecular pathway analysis of HER2 and JNK1/2/3 of EA extract exposed cells revealed that it can block HER2 and JNK1/2/3 activities, which could be the major molecular pathway behind these events. Our findings implicate that EA extract may possess chemo-preventive effects against HER2-positive breast cancer via HER2 inactivation and specifically JNK1/2/3 signaling pathways.
Keywords: EMT; Elaeagnus angustifolia; apoptosis; breast cancer; chemoprevention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
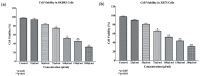
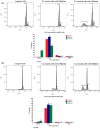
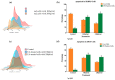
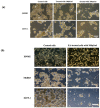
References
-
- Sareyeldin R.M., Gupta I., Al-Hashimi I., Al-Thawadi H.A., Al Farsi H.F., Vranic S., Al Moustafa A.-E. Gene Expression and miRNAs Profiling: Function and Regulation in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2)-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2019;11:646. doi: 10.3390/cancers11050646. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giordano S.H., Temin S., Chandarlapaty S., Crews J.R., Esteva F.J., Kirshner J.J., Krop I.E., Levinson J., Lin N.U., Modi S., et al. Systemic Therapy for Patients with Advanced Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Positive Breast Cancer: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:2736–2740. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.79.2697. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

