Thaumatin-Like Protein (TLP) Gene Family in Barley: Genome-Wide Exploration and Expression Analysis during Germination
- PMID: 32947963
- PMCID: PMC7564728
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11091080
Thaumatin-Like Protein (TLP) Gene Family in Barley: Genome-Wide Exploration and Expression Analysis during Germination
Abstract
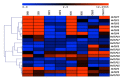
Thaumatin-like Proteins (TLPs) are known to play a vital role in plant defense, developmental processes and seed germination. We identified 19 TLP genes from the reference genome of barley and 37, 28 and 35 TLP genes from rice, Brachypodium and sorghum genomes, respectively. Comparative phylogenetic analysis classified the TLP family into nine groups. Localized gene duplications with diverse exon/intron structures contributed to the expansion of the TLP gene family in cereals. Most of the barley TLPs were localized on chromosome 5H. The spatiotemporal expression pattern of HvTLP genes indicated their predominant expression in the embryo, developing grains, root and shoot tissues. Differential expression of HvTLP14, HvTLP17 and HvTLP18 in the malting variety (Morex) over 16-96 h of grain germination revealed their possible role in malting. This study provides a description of the TLP gene family in barley and their possible involvement in seed germination and the malting process.
Keywords: barley; cereals; expression analysis; phylogenetics; thaumatin like-proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Co-bombardment, integration and expression of rice chitinase and thaumatin-like protein genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare cv. Conlon).Plant Cell Rep. 2007 May;26(5):631-9. doi: 10.1007/s00299-006-0263-x. Epub 2006 Nov 11. Plant Cell Rep. 2007. PMID: 17103003
-
Cloning and characterization of SOC1 homologs in barley (Hordeum vulgare) and their expression during seed development and in response to vernalization.Physiol Plant. 2012 Sep;146(1):71-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01610.x. Epub 2012 May 10. Physiol Plant. 2012. PMID: 22409646
-
Advancing Sustainable Malting Practices: Aquaporins as Potential Breeding Targets for Improved Water Uptake during Controlled Germination of Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).J Agric Food Chem. 2024 May 1;72(17):10149-10161. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c00884. Epub 2024 Apr 18. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38635353 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Thaumatin-like Proteins: Function, Evolution and Biotechnological Applications.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(1):36-51. doi: 10.2174/1389203720666190318164905. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 30887921 Review.
-
Insights on the Proteases Involved in Barley and Wheat Grain Germination.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 28;20(9):2087. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092087. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31035313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In silico characterization of differentially expressed short-read nucleotide sequences identified in dieback stress-induced transcriptomic analysis reveals their role as antimicrobial peptides.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 20;14:1168221. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1168221. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37021314 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis provides insights into the role of TLP16 in Musa acuminata Resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense wilt.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jan 22;25(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-06032-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39844040 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the TLP Gene Family in Phyllostachys edulis and Association with Witches' Broom Disease Resistance in Bamboo.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 17;24(12):10257. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210257. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373405 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analyses of Thaumatin-like Protein Family Genes Reveal the Involvement in the Response to Low-Temperature Stress in Ammopiptanthus nanus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 22;24(3):2209. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032209. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768531 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV2 infectivity is potentially modulated by host redox status.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020;18:3705-3711. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.11.016. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 33250972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brandazza A., Angeli S., Tegoni M., Cambillau C., Pelosi P. Plant stress proteins of the thaumatin-like family discovered in animals. FEBS Lett. 2004;572:3–7. - PubMed
-
- van Loon L.C., Rep M. Pieterse CM: Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2006;44:135–162. - PubMed
-
- Velazhahan R., Datta S.K., Muthukrishnan S. Pathogenesis-Related Proteins in Plants. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 1999. The PR-5 family: Thaumatin-like proteins; pp. 107–129.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

