Drugs Modulating CD4+ T Cells Blood-Brain Barrier Interaction in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 32948022
- PMCID: PMC7558445
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12090880
Drugs Modulating CD4+ T Cells Blood-Brain Barrier Interaction in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
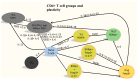
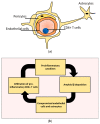
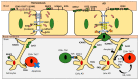
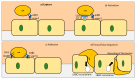
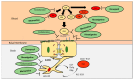
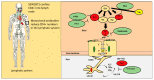
The effect of Alzheimer's disease (AD) medications on CD4+ T cells homing has not been thoroughly investigated. CD4+ T cells could both exacerbate and reduce AD symptoms based on their infiltrating subpopulations. Proinflammatory subpopulations such as Th1 and Th17 constitute a major source of proinflammatory cytokines that reduce endothelial integrity and stimulate astrocytes, resulting in the production of amyloid β. Anti-inflammatory subpopulations such as Th2 and Tregs reduce inflammation and regulate the function of Th1 and Th17. Recently, pathogenic Th17 has been shown to have a superior infiltrating capacity compared to other major CD4+ T cell subpopulations. Alzheimer's drugs such as donepezil (Aricept), rivastigmine (Exelon), galantamine (Razadyne), and memantine (Namenda) are known to play an important part in regulating the mechanisms of the neurotransmitters. However, little is known about the effect of these drugs on CD4+ T cell subpopulations' infiltration of the brain during AD. In this review, we focus on understanding the influence of AD drugs on CD4+ T cell subpopulation interactions with the BBB in AD. While current AD therapies improve endothelial integrity and reduce astrocytes activations, they vary according to their influence on various CD4+ T cell subpopulations. Donepezil reduces the numbers of Th1 but not Th2, Rivastigmine inhibits Th1 and Th17 but not Th2, and memantine reduces Th1 but not Treg. However, none of the current AD drugs is specifically designed to target the dysregulated balance in the Th17/Treg axis. Future drug design approaches should specifically consider inhibiting CD4+ Th17 to improve AD prognosis.
Keywords: Alzheimer; CD4+ T cells; Th17; blood brain barrier; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors would like to declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parkinson's disease patients have a complex phenotypic and functional Th1 bias: cross-sectional studies of CD4+ Th1/Th2/T17 and Treg in drug-naïve and drug-treated patients.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Jul 12;15(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1248-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30001736 Free PMC article.
-
PR-957 Suppresses Th1 and Th17 Cell Differentiation via Inactivating PI3K/AKT Pathway in Alzheimer's Disease.Neuroscience. 2023 Feb 1;510:82-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.10.021. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Neuroscience. 2023. PMID: 36581132
-
Shenghua Decoction reduces uterine bleeding and regulates T-cell paradigm in human deciduas of RU486 medical abortion.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):907-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.033. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24140602 Clinical Trial.
-
CD4+ T Cell Fate in Glomerulonephritis: A Tale of Th1, Th17, and Novel Treg Subtypes.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:5393894. doi: 10.1155/2016/5393894. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27974866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green tea EGCG, T cells, and T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.Mol Aspects Med. 2012 Feb;33(1):107-18. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2011.10.001. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Mol Aspects Med. 2012. PMID: 22020144 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Exploration of Immunity-Related Genes and Natural Products for Alzheimer's Disease Based on Bioinformatics, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025 Apr;13(4):e70166. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70166. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025. PMID: 40192032 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on the Evolutionary History of Bregs.Genes (Basel). 2022 May 17;13(5):890. doi: 10.3390/genes13050890. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of BDNF and CD4 + T cell crosstalk on depression.Immunol Res. 2024 Oct;72(5):883-894. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09514-4. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38980567 No abstract available.
-
The Current Landscape of Hypotheses Describing the Contribution of CD4+ Heterogeneous Populations to ALS.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 23;46(8):7846-7861. doi: 10.3390/cimb46080465. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39194682 Free PMC article.
-
Factors regulating the differences in frequency of infiltration of Th17 and Treg of the blood-brain barrier.Immunogenetics. 2023 Oct;75(5):417-423. doi: 10.1007/s00251-023-01310-y. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Immunogenetics. 2023. PMID: 37430007 Review.
References
-
- Saresella M., Calabrese E., Marventano I., Piancone F., Gatti A., Alberoni M., Nemni R., Clerici M. Increased activity of Th-17 and Th-9 lymphocytes and a skewing of the post-thymic differentiation pathway are seen in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011;25:539–547. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.12.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

