A computational approach to drug repurposing against SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)
- PMID: 32948103
- PMCID: PMC7544925
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1822209
A computational approach to drug repurposing against SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)
Abstract
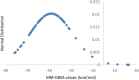
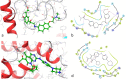
The spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) caused a worldwide outbreak of coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), which rapidly evolved as a global concern. The efforts of the scientific community are pointed towards the identification of promptly available therapeutic options. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) is a promising target for developing small molecules to contrast SARS-CoV-2 replication. Modern computational tools can boost identification and repurposing of known drugs targeting RdRp. We here report the results regarding the screening of a database containing more than 8800 molecules, including approved, experimental, nutraceutical, illicit, withdrawn and investigational compounds. The molecules were docked against the cryo-electron microscopy structure of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp, optimized by means of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The adopted three-stage ensemble docking study underline that compounds formerly developed as kinase inhibitors may interact with RdRp.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Keywords: RdRp; SARS-CoV-2; molecular modelling; remdesivir; repurposing.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of FDA approved drugs against SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro), drug repurposing approach.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111544. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111544. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34311539 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors using pharmacophore modelling, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation approaches.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40(24):13366-13377. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1987329. Epub 2021 Oct 12. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 34637693
-
Plant-derived natural polyphenols as potential antiviral drugs against SARS-CoV-2 via RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibition: an in-silico analysis.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 Oct;39(16):6249-6264. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1796810. Epub 2020 Jul 28. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021. PMID: 32720577 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the potential of natural compounds as novel inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RdRP using computational approaches.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2024 Nov;40(3):1535-1555. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2195240. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2024. PMID: 36994810 Review.
-
State-of-the-Art Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies of RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase of SARS-CoV-2.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 8;23(18):10358. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810358. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142270 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
First report on chemometrics-driven multilayered lead prioritization in addressing oxysterol-mediated overexpression of G protein-coupled receptor 183.Mol Divers. 2024 Dec;28(6):4199-4220. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10811-1. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 38460065
-
Dynamic properties of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerases studied by molecular dynamics simulations.Chem Phys Lett. 2021 Sep;778:138819. doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138819. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Chem Phys Lett. 2021. PMID: 34127868 Free PMC article.
-
Potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID 19) proteases PLpro and Mpro/ 3CLpro: molecular docking and simulation studies of three pertinent medicinal plant natural components.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021;2:100038. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100038. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34870149 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Management with Repurposing Approaches: A Mystery During COVID-19 Outbreak.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(6):712-733. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230613141746. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37312440 Review.
-
Identifying and repurposing antiviral drugs against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with in silico and in vitro approaches.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 29;538:137-144. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.094. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33272566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beigel, J. H., Tomashek, K. M., Dodd, L. E., Mehta, A. K., Zingman, B. S., Kalil, A. C., Hohmann, E., Chu, H. Y., Luetkemeyer, A., Kline, S., Lopez de Castilla, D., Finberg, R. W., Dierberg, K., Tapson V., Hsieh, L., Patterson, T. F., Paredes, R., Sweeney, D. A., Short, W. R., … Lane, H. C. (2020). Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—Preliminary Report. New England Journal of Medicine. 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bettiol, A., Marconi, E., Lombardi, N., Crescioli, G., Gherlinzoni, F., Walley, T., Vannacci, A., Chinellato, A., & Giusti, P. (2018). Pattern of use and long-term safety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A decade of real-world management of chronic myeloid leukemia. Clinical Drug Investigation, 38(9), 837–844. 10.1007/s40261-018-0676-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
