Dynamics of the transcriptome during chicken embryo development based on primordial germ cells
- PMID: 32948222
- PMCID: PMC7501632
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-020-05286-w
Dynamics of the transcriptome during chicken embryo development based on primordial germ cells
Abstract
Objective: Regulation of gene expression during embryo development on the basis of migration of primordial germ cells (PGCs) in vivo has been rarely studied due to limited cell number and the necessity to isolate PGCs from a large number of embryos. Moreover, little is known about the comprehensive dynamics of the transcriptome in chicken PGCs during early developmental stages. The current study investigated transcriptome dynamics of chicken PGCs at key developmental stages: 4.5, 8 and 12 days of embryo incubation. PGCs were collected, and RNA was isolated using a commercial kit for single cells. The isolated RNA was subjected to microarray analysis (Agilent Technologies).
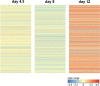
Results: Between 8 and 12 days of incubation, the highest number of genes was regulated. These data indicate that the most intense biological activity occurs between 8 and 12 days of embryo development. Heat map showed a significant decrease in gene expression on day 8, while it increased on day 12. The development of a precise method to isolate bird PGCs as well as the method to isolate RNA from single cells isolated from one embryo allows for early molecular analysis and detection of transcriptome changes during embryonic development.
Keywords: Gene expression; Microarray; Primordial germ cells; White Leghorn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the Transcriptomic and Epigenetic Profiles of Gonadal Primordial Germ Cells of White Leghorn and Green-Legged Partridgelike Chicken Embryos.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 19;12(7):1090. doi: 10.3390/genes12071090. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356106 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Chicken Primordial Germ Cells and Their Application in Transgenesis.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1650:229-242. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7216-6_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28809025
-
Expression and knockdown analysis of glucose phosphate isomerase in chicken primordial germ cells.Biol Reprod. 2012 Sep 13;87(3):57. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.112.101345. Print 2012 Sep. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22699485
-
The early development of germ cells in chicken.Int J Dev Biol. 2018;62(1-2-3):145-152. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.170283jh. Int J Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29616722 Review.
-
Development, differentiation and manipulation of chicken germ cells.Dev Growth Differ. 2013 Jan;55(1):20-40. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12026. Dev Growth Differ. 2013. PMID: 23294359 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Transcriptomic and Epigenetic Profiles of Gonadal Primordial Germ Cells of White Leghorn and Green-Legged Partridgelike Chicken Embryos.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 19;12(7):1090. doi: 10.3390/genes12071090. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356106 Free PMC article.
-
Chicken embryo as a model in epigenetic research.Poult Sci. 2021 Jul;100(7):101164. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101164. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Poult Sci. 2021. PMID: 34058565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of genes involved in brain development: insights into the organization and evolution of the telencephalic pallium.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 13;14(1):6102. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51964-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38480729 Free PMC article.
-
Germline stem cells in human.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Oct 2;7(1):345. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01197-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36184610 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eyal-Giladi H, Ginsburg M, Farbarov A. Avian primordial germ cells are of epiblastic origin. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981;65:139–147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

