Ascorbate-induced oxidative stress mediates TRP channel activation and cytotoxicity in human etoposide-sensitive and -resistant retinoblastoma cells
- PMID: 32948812
- PMCID: PMC7758186
- DOI: 10.1038/s41374-020-00485-2
Ascorbate-induced oxidative stress mediates TRP channel activation and cytotoxicity in human etoposide-sensitive and -resistant retinoblastoma cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: Ascorbate-induced oxidative stress mediates TRP channel activation and cytotoxicity in human etoposide-sensitive and -resistant retinoblastoma cells.Lab Invest. 2021 Aug;101(8):1112. doi: 10.1038/s41374-020-00499-w. Lab Invest. 2021. PMID: 34145382 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
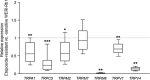
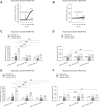
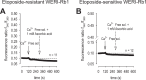
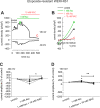
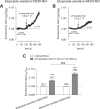
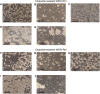
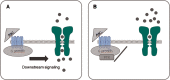
There are indications that pharmacological doses of ascorbate (Asc) used as an adjuvant improve the chemotherapeutic management of cancer. This favorable outcome stems from its cytotoxic effects due to prooxidative mechanisms. Since regulation of intracellular Ca2+ levels contributes to the maintenance of cell viability, we hypothesized that one of the effects of Asc includes disrupting regulation of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis. Accordingly, we determined if Asc induced intracellular Ca2+ influx through activation of pertussis sensitive Gi/o-coupled GPCR which in turn activated transient receptor potential (TRP) channels in both etoposide-resistant and -sensitive retinoblastoma (WERI-Rb1) tumor cells. Ca2+ imaging, whole-cell patch-clamping, and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) were performed in parallel with measurements of RB cell survival using Trypan Blue cell dye exclusion. TRPM7 gene expression levels were similar in both cell lines whereas TRPV1, TRPM2, TRPA1, TRPC5, TRPV4, and TRPM8 gene expression levels were downregulated in the etoposide-resistant WERI-Rb1 cells. In the presence of extracellular Ca2+, 1 mM Asc induced larger intracellular Ca2+ transients in the etoposide-resistant WERI-Rb1 than in their etoposide-sensitive counterpart. With either 100 µM CPZ, 500 µM La3+, 10 mM NAC, or 100 µM 2-APB, these Ca2+ transients were markedly diminished. These inhibitors also had corresponding inhibitory effects on Asc-induced rises in whole-cell currents. Pertussis toxin (PTX) preincubation blocked rises in Ca2+ influx. Microscopic analyses showed that after 4 days of exposure to 1 mM Asc cell viability fell by nearly 100% in both RB cell lines. Taken together, one of the effects underlying oxidative mediated Asc-induced WERI-Rb1 cytotoxicity stems from its promotion of Gi/o coupled GPCR mediated increases in intracellular Ca2+ influx through TRP channels. Therefore, designing drugs targeting TRP channel modulation may be a viable approach to increase the efficacy of chemotherapeutic treatment of RB. Furthermore, Asc may be indicated as a possible supportive agent in anti-cancer therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Joint CB1 and NGF Receptor Activation Suppresses TRPM8 Activation in Etoposide-Resistant Retinoblastoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 31;25(3):1733. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031733. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339011 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Profiling of WERI-RB1 and Etoposide-Resistant WERI-ETOR Reveals New Insights into Topoisomerase Inhibitor Resistance in Retinoblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 6;23(7):4058. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074058. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409416 Free PMC article.
-
Altered calcium regulation by thermosensitive transient receptor potential channels in etoposide-resistant WERI-Rb1 retinoblastoma cells.Exp Eye Res. 2012 Jan;94(1):157-73. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2011.12.002. Epub 2011 Dec 11. Exp Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 22182671
-
Targeted pharmacologic inhibition of S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2) mediated cell cycle regulation in lung and other RB-Related cancers: A brief review of current status and future prospects.Adv Biol Regul. 2023 May;88:100964. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2023.100964. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Adv Biol Regul. 2023. PMID: 37004354 Review.
-
The role of TRP channels in oxidative stress-induced cell death.J Membr Biol. 2006 Jan;209(1):31-41. doi: 10.1007/s00232-005-0839-3. Epub 2006 Apr 17. J Membr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16685599 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Biological Research on the Pathogenic Mechanism of Retinoblastoma.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 May 27;46(6):5307-5321. doi: 10.3390/cimb46060317. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38920989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joint CB1 and NGF Receptor Activation Suppresses TRPM8 Activation in Etoposide-Resistant Retinoblastoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 31;25(3):1733. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031733. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339011 Free PMC article.
-
Relevant Membrane Transport Proteins as Possible Gatekeepers for Effective Pharmacological Ascorbate Treatment in Cancer.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 12;12(4):916. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040916. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of transient receptor potential channels in ocular diseases: a narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Aug;10(15):839. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6145. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36034986 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Profiling of WERI-RB1 and Etoposide-Resistant WERI-ETOR Reveals New Insights into Topoisomerase Inhibitor Resistance in Retinoblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 6;23(7):4058. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074058. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Control UfIC. RETINOBLASTOMA. review of cancer medicines on the WHO list of essential medicines. WHO; 2014.https://www.who.int/selection_medicines/committees/expert/20/application....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

