GWA-based pleiotropic analysis identified potential SNPs and genes related to type 2 diabetes and obesity
- PMID: 32948839
- PMCID: PMC7884093
- DOI: 10.1038/s10038-020-00843-4
GWA-based pleiotropic analysis identified potential SNPs and genes related to type 2 diabetes and obesity
Abstract
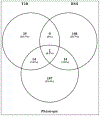
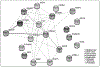
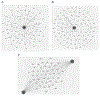
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of symptoms including excessive body fat and insulin resistance which may lead to obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D). The physiological and pathological cross-talk between T2D and obesity is crucial and complex, meanwhile, the genetic connection between T2D and obesity is largely unknown. The purpose of this study is to identify pleiotropic SNPs and genes between these two associated conditions by applying genetic analysis incorporating pleiotropy and annotation (GPA) on two large genome-wide association studies (GWAS) data sets: a body mass index (BMI) data set containing 339,224 subjects and a T2D data set containing 110,452 subjects. In all, 5182 SNPs showed pleiotropy in both T2D and obesity. After further prioritization based on suggested local false discovery rates (FDR) by the GPA model, 2146 SNPs corresponding to 217 unique genes are significantly associated with both traits (FDR < 0.2), among which 187 are newly identified pleiotropic genes compare with original GWAS in individual traits. Subsequently, gene enrichment and pathway analyses highlighted several pleiotropic SNPs including rs849135 (FDR = 0.0002), rs2119812 (FDR = 0.0018), rs4506565 (FDR = 1.23E-08), rs1558902 (7.23E-10) and corresponding genes JAZF1, SYN2, TCF7L2, FTO which may play crucial rol5es in the etiology of both T2D and obesity. Additional evidences from expression data analysis of pleiotropic genes strongly supports that the pleiotropic genes including JAZF1 (p = 1.39E-05 and p = 2.13E-05), SYN2 (p = 5.49E-03 and p = 5.27E-04), CDKN2C (p = 1.99E-12 and p = 6.27E-11), RABGAP1 (p = 3.08E-03 and p = 7.46E-03), and UBE2E2 (p = 1.83E-04 and p = 8.22E-03) play crucial roles in both obesity and T2D pathogenesis. Pleiotropic analysis integrated with functional network identified several novel and causal SNPs and genes involved in both BMI and T2D which may be ignored in single GWAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased identification of novel variants in type 2 diabetes, birth weight and their pleiotropic loci.J Diabetes. 2017 Oct;9(10):898-907. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12510. Epub 2017 Jan 20. J Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 27896934 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel variants associated with osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes and potentially pleiotropic loci using pleiotropic cFDR method.Bone. 2018 Dec;117:6-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.08.020. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Bone. 2018. PMID: 30172742 Free PMC article.
-
Additional common variants associated with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease detected using a pleiotropic cFDR method.J Diabetes Complications. 2018 Dec;32(12):1105-1112. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 9. J Diabetes Complications. 2018. PMID: 30270018 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate analysis of genome-wide data to identify potential pleiotropic genes for type 2 diabetes, obesity and coronary artery disease using MetaCCA.Int J Cardiol. 2019 May 15;283:144-150. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.10.102. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Int J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30459114 Review.
-
Comprehensive identification of pleiotropic loci for body fat distribution using the NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies.Obes Rev. 2019 Mar;20(3):385-406. doi: 10.1111/obr.12806. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Obes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30565845 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiometabolic Traits in Adult Twins: Heritability and BMI Impact with Age.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 29;15(1):164. doi: 10.3390/nu15010164. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36615821 Free PMC article.
-
Multipartite network analysis to identify environmental and genetic associations of metabolic syndrome in the Korean population.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 31;14(1):20283. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71217-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39217223 Free PMC article.
-
JAZF1: A metabolic actor subunit of the NuA4/TIP60 chromatin modifying complex.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Apr 7;11:1134268. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1134268. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37091973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide association study reveals novel loci associated with feeding behavior in Pekin ducks.BMC Genomics. 2021 May 8;22(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07668-1. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33964893 Free PMC article.
-
E-GWAS: an ensemble-like GWAS strategy that provides effective control over false positive rates without decreasing true positives.Genet Sel Evol. 2023 Jul 5;55(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12711-023-00820-3. Genet Sel Evol. 2023. PMID: 37407918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fall T, Ingelsson E. Genome-wide association studies of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014;382:740–57. - PubMed
-
- Kolovou GD, Anagnostopoulou KK, Salpea KD, Mikhailidis DP. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in various populations. Am J Med Sci. 2007;333:362–71. - PubMed
-
- Desroches S, Lamarche B. The evolving definitions and increasing prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2007;32:23–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
