Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of a new flex-rigid pleuroscope
- PMID: 32949105
- PMCID: PMC7891332
- DOI: 10.1111/crj.13274
Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of a new flex-rigid pleuroscope
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Clin Respir J. 2022 Dec;16(12):849. doi: 10.1111/crj.13550. Clin Respir J. 2022. PMID: 36458823 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
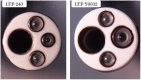
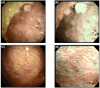
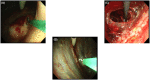
Objective: New flex-rigid pleuroscope enables observations with a maximum angle of curvature of 180° , allowing visualization of the area near the insertion site of the pleuroscope. And, it improved the image quality and channel inner diameter. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and safety of a new flex-rigid pleuroscope.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of patients who were examined with a new flex-rigid pleuroscope under local anesthesia at our institution was conducted. Pleuroscopy was performed in 33 patients with undiagnosed exudative pleural effusions from December 2016 to March 2019.
Results: A total of 33 patients (10 women, 23 men); their median age 74 years (range 24-90) were investigated. Pleuroscopy showed that 18 had malignant pleural disease (54%), and 15 had benign pleural diseases (46%). The top three most frequent causes of pleural disease were pleural metastases of lung carcinoma (30.3%), pyothorax (15.1%), and malignant pleural mesothelioma (12.1%). In 32 cases (97%), observation at the introducer insertion site was possible. It was not possible in one case due to hard adhesions. The diagnostic rate was 100%, and the complication rate was 6.1%. There were no major complications, and minor complications included mild pain (one case) and minor bleeding (one case) that was stanched spontaneously.
Conclusions: The new flex-rigid pleuroscope is effective and safe for diagnosing pleural effusions. The improved bending angle is likely to minimize the blind area. The new pleuroscopy fiberscope may improve the diagnostic rate.
Keywords: LTF-Y0032; flex-rigid pleuroscope; pleural biopsy; pleural effusion.
© 2020 The Authors. The Clinical Respiratory Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Olympus lent the authors department the LTF‐Y0032 pleuroscope and CV‐290 endoscopy system. The authors have stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article, respectively.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Flex-rigid pleuroscopy under local anesthesia in patients with dry pleural dissemination on radiography.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014 Aug;44(8):749-55. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyu078. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24907385
-
Diagnostic Utility of Pleural Fluid Cell Block versus Pleural Biopsy Collected by Flex-Rigid Pleuroscopy for Malignant Pleural Disease: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 23;11(11):e0167186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167186. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27880851 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized trial comparing the diagnostic yield of rigid and semirigid thoracoscopy in undiagnosed pleural effusions.Respir Care. 2014 May;59(5):756-64. doi: 10.4187/respcare.02738. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Respir Care. 2014. PMID: 24106326 Clinical Trial.
-
Evolution of semi-rigid thoracoscopy.Indian J Tuberc. 2022 Jan;69(1):12-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2021.03.002. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Indian J Tuberc. 2022. PMID: 35074144 Review.
-
Pleuroscopy for the Diagnosis of Cancer in Patients with Pleural Effusion: A Review of the Diagnostic Accuracy, Safety, Cost-Effectiveness and Guidelines [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2020 Apr 16. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2020 Apr 16. PMID: 33074637 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting Visceral Pleural Invasion in Resected Lung Adenocarcinoma via Computed Tomography.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 23;17(9):1414. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091414. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361342 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of the utility of cryobiopsy for tuberculous pleurisy in thoracoscopy: A report of seven cases.Respir Med Case Rep. 2023 Mar 24;43:101840. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2023.101840. eCollection 2023. Respir Med Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37064571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kendall S, Bryan AJ, Large SR, et al. Pleural effusions: is thoracoscopy a reliable investigation? A retrospective review. Respir Med. 1992;86:437‐440. - PubMed
-
- Von Hoff D.Di Volsi V. Diagnostic reliability of needle biopsy of the parietal pleura: a review of 272 biopsies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979;72:48‐51. - PubMed
-
- Poe R, Israel R, Utell M, et al. Sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of closed pleural biopsy. Arch Intern Med. 1984;144:325‐328. - PubMed
-
- Schonfeld N, Loddenkemper R . Pleural biopsy and thoracoscopy. Eur Respir Mon. 1998;9:135‐152.
-
- Sakuraba M, Masuda K, Hebisawa A, et al. Diagnostic value of thoracoscopic pleural biopsy for pleurisy under local anesthesia. ANZ J Surg. 2006;76:722‐724. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

