In Vivo HSC Gene Therapy Using a Bi-modular HDAd5/35++ Vector Cures Sickle Cell Disease in a Mouse Model
- PMID: 32949495
- PMCID: PMC7854285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.09.001
In Vivo HSC Gene Therapy Using a Bi-modular HDAd5/35++ Vector Cures Sickle Cell Disease in a Mouse Model
Abstract
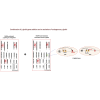
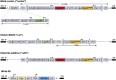
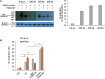
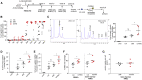
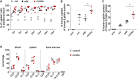
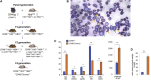
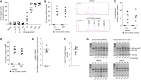
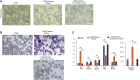
We have recently reported that, after in vivo hematopoietic stem cell/progenitor (HSPC) transduction with HDAd5/35++ vectors, SB100x transposase-mediated γ-globin gene addition achieved 10%-15% γ-globin of adult mouse globin, resulting in significant but incomplete phenotypic correction in a thalassemia intermedia mouse model. Furthermore, genome editing of a γ-globin repressor binding site within the γ-globin promoter by CRISPR-Cas9 results in efficient reactivation of endogenous γ-globin. Here, we aimed to combine these two mechanisms to obtain curative levels of γ-globin after in vivo HSPC transduction. We generated a HDAd5/35++ adenovirus vector (HDAd-combo) containing both modules and tested it in vitro and after in vivo HSPC transduction in healthy CD46/β-YAC mice and in a sickle cell disease mouse model (CD46/Townes). Compared to HDAd vectors containing either the γ-globin addition or the CRISPR-Cas9 reactivation units alone, in vivo HSC transduction of CD46/Townes mice with the HDAd-combo resulted in significantly higher γ-globin in red blood cells, reaching 30% of that of adult human α and βS chains and a complete phenotypic correction of sickle cell disease.
Copyright © 2020 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
A "Shot in the Arm" for Sickle Cell Disease.Mol Ther. 2021 Feb 3;29(2):416-417. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.01.009. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Mol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33472029 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Conley C.L., Weatherall D.J., Richardson S.N., Shepard M.K., Charache S. Hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin: a study of 79 affected persons in 15 Negro families in Baltimore. Blood. 1963;21:261–281. - PubMed
-
- Stamatoyannopoulos G., Wood W.G., Papayannopoulou T., Nute P.E. A new form of hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin in blacks and its association with sickle cell trait. Blood. 1975;46:683–692. - PubMed
-
- Kanter J., Thompson A.A., Mapara M.Y., Kwiatkowski J.L., Krishnamurti L., Schmidt M., Miller A.L., Pierciey F.J., Huang W., Ribeil J.-A. Updated Results From The Hgb-206 Study In Patients With Severe Sickle Cell Disease Treated Under A Revised Protocol With Lentiglobin Gene Therapy Using Plerixafor-Mobilised Haematopoietic Stem Cells. HemaSphere. 2019;3:754–755.
-
- Anurathapan U., Pakakasama S., Mekjaruskul P., Sirachainan N., Songdej D., Chuansumrit A., Charoenkwan P., Jetsrisuparb A., Sanpakit K., Pongtanakul B. Outcomes of thalassemia patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation by using a standard myeloablative versus a novel reduced-toxicity conditioning regimen according to a new risk stratification. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:2066–2071. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

