Protective effects of HY1702 on lipopolysaccharide-induced mild acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice
- PMID: 32949601
- PMCID: PMC8368985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173563
Protective effects of HY1702 on lipopolysaccharide-induced mild acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice
Abstract
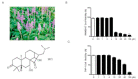
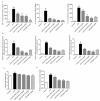
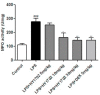
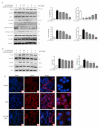
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is an inflammatory disease with no effective pharmacological treatment. We investigated the therapeutic effect of HY1702, a new small molecule diterpene obtained from the processing and modification of Glaucocalyxin A and may exhibit anti-inflammatory activity. Specifically, we studied the anti-inflammatory effects of HY1702 on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 and THP-1 cells in vitro and its protective efficacy on lipopolysaccharide-induced mild acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice. Our results showed that HY1702 significantly decreased lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokine expression in RAW264.7 and THP-1 cells and attenuated the secretion of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 by down-regulating the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase 2 in RAW264.7 cells. In mice with lipopolysaccharide-induced mild acute respiratory distress syndrome, HY1702 alleviated histological alterations in the lungs and reduced the alveolar cavity protein leakage and inflammatory cytokine expression in murine bronchial alveolar lavage fluid. HY1702 decreased the myeloperoxidase activity and lung wet to dry weight ratio. In our mechanism studies in lipopolysaccharide-exposed RAW264.7 cells, HY1702 suppressed the inflammation stimulated by lipopolysaccharide through inhibiting phosphorylation of inhibitor of nuclear factor κB kinase subunit α/β (IKKα/β) and inhibitor of nuclear factor κB subunit α (IκBα), further affecting the nuclear transfer of phosphorylated p65. Meanwhile, phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) was inhibited. These data suggest that HY1702 can reduce inflammation on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages and attenuate the symptoms of mild acute respiratory distress syndrome in a murine model by regulating the nuclear factor κB and MAP kinase signalling pathways.
Keywords: HY1702; Inflammation; MAP kinase; Mild acute respiratory distress syndrome; Nuclear factor κB.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
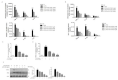

Similar articles
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock and inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages via the p38/ERK and NF-kappaB pathways.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(11):2572-82. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.05.005. Epub 2008 May 15. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18571461
-
Ethyl acetate fraction from Nymphaea hybrida Peck modulates inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and acute inflammation murine models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113698. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113698. Epub 2020 Dec 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33338590
-
Schisantherin A exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by down-regulating NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW 264.7 cells.Inflammation. 2010 Apr;33(2):126-36. doi: 10.1007/s10753-009-9166-7. Inflammation. 2010. PMID: 20238486
-
Ligustilide prevents LPS-induced iNOS expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages by preventing ROS production and down-regulating the MAPK, NF-κB and AP-1 signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Sep;11(9):1166-72. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.03.014. Epub 2011 Mar 30. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21457761
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Fluoroquinolones in Community-Acquired Pneumonia-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 29;12(4):761. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040761. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672119 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipocalin-2 silencing suppresses inflammation and oxidative stress of acute respiratory distress syndrome by ferroptosis via inhibition of MAPK/ERK pathway in neonatal mice.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):508-520. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2009970. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 34969358 Free PMC article.
-
DGA ameliorates severe acute pancreatitis through modulating macrophage pyroptosis.Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct;73(10):1803-1817. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01931-3. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39231819
-
The Association Between the Baseline and the Change in Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Short-Term Mortality in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 May 14;8:636869. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.636869. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34055826 Free PMC article.
-
[2, 3, 5, 4'-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d-glucoside alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 Jul 20;41(7):1101-1106. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.07.20. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34308863 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Glaucocalyxin A alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells and permeability injury by inhibiting STAT3 signaling.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Apr;23(4):313. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11242. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35369532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham E. Neutrophils and acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2003;31:S195–199. - PubMed
-
- Babich H., Palace M.R., Stern A. Oxidative stress in fish cells: in vitro studies. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1993;24:173–178. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia M., Moochhala S. Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Pathol. 2004;202:145–156. - PubMed
-
- Chen T., Mou Y., Tan J., Wei L., Qiao Y., Wei T., Xiang P., Peng S., Zhang Y., Huang Z. The protective effect of CDDO-Me on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int. Immunopharm. 2015;25:55–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

