Impact of interleukin-6 blockade with tocilizumab on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and antibody responses in patients with COVID-19: A prospective cohort study
- PMID: 32950003
- PMCID: PMC7492814
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999
Impact of interleukin-6 blockade with tocilizumab on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and antibody responses in patients with COVID-19: A prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: The virological and immunological effects of the immunomodulatory drugs used for COVID-19 remain unknown. We evaluated the impact of interleukin (IL)-6 blockade with tocilizumab on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and the antibody response in patients with COVID-19.
Methods: Prospective cohort study in patients admitted with COVID-19. Serial nasopharyngeal and plasma samples were measured for SARS-CoV-2 RNA and S-IgG/N-IgG titers, respectively.
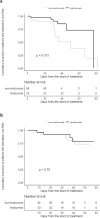
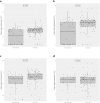
Findings: 138 patients with confirmed infection were included; 76 (55%) underwent IL-6 blockade. Median initial SOFA (p = 0•016) and SARS-CoV-2 viral load (p<0•001, Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test) were significantly higher among anti-IL-6 users. Patients under IL-6 blockade showed delayed viral clearance in the Kaplan-Meier curves (HR 0•35 [95%CI] [0•15-0•81], log-rank p = 0•014), but an adjusted propensity score matching model did not demonstrate a significant relationship of IL-6 blockade with viral clearance (HR 1•63 [0•35-7•7]). Cox regression showed an inverse association between SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and the initial viral load (HR 0•35 [0•11-0•89]). Patients under the IL-6 blocker showed shorter median time to seropositivity, higher peak antibody titers, and higher cumulative proportion of seropositivity in the Kaplan Meier curves (HR 3•1 [1•9-5] for S-IgG; and HR 3•0 [1•9-4•9] for N-IgG; log-rank p<0•001 for both). However, no significant differences between groups were found in either S-IgG (HR 1•56 [0•41-6•0]) nor N-IgG (HR 0•96 [0•26-3•5]) responses in an adjusted propensity score analysis.
Interpretation: Our results suggest that in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, IL-6 blockade does not impair the viral specific antibody responses. Although a delayed viral clearance was observed, it was driven by a higher initial viral load. The study supports the safety of this therapy in patients with COVID-19.
Funding: Instituto de salud Carlos III (Spain).
Keywords: Anti-cytokine therapy; Antibody responses; COVID-19; N-IgG; S-IgG; SARS-CoV-2; Tocilizumab; Viral kinetics.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interests Dr. Gutiérrez reports personal fees from Janssen-Cilag and from ViiV Health Care, outside the submitted work. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Comment in
-
Tocilizumab is recommended for the treatment of severe COVID-19.EBioMedicine. 2020 Nov;61:103045. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103045. Epub 2020 Oct 7. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 33038768 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mihara M., Kasutani K., Okazaki M. Tocilizumab inhibits signal transduction mediated by both mIL-6R and sIL-6R, but not by the receptors of other members of IL-6 cytokine family. Int Immunopharmacol. 2005;5:1731–1740. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

