miR-204-3p/Nox4 Mediates Memory Deficits in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 32950103
- PMCID: PMC7791017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.09.006
miR-204-3p/Nox4 Mediates Memory Deficits in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
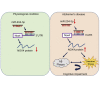
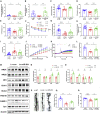
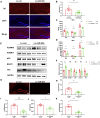
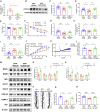
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder leading to dementia in the elderly, and the mechanisms of AD are not fully defined. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been shown to contribute to memory deficits in AD. In this study, we identified that miR-204-3p was downregulated in the hippocampus and plasma of 6-month-old APPswe/PS1dE9 (APP/PS1) mice. miR-204-3p overexpression attenuated memory and synaptic deficits in APP/PS1 mice. The amyloid levels and oxidative stress were decreased in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice after miR-204-3p overexpression. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase 4 (Nox4) was a target of miR-204-3p, and Nox4 inhibition by GLX351322 protected neuronal cells against Aβ1-42-induced neurotoxicity. Furthermore, GLX351322 treatment rescued synaptic and memory deficits, and decreased oxidative stress and amyloid levels in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice. These results revealed that miR-204-3p attenuated memory deficits and oxidative stress in APP/PS1 mice by targeting Nox4, and miR-204-3p overexpression and/or Nox4 inhibition might be a potential therapeutic strategy for AD treatment.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Nox4; beta amyloid; memory deficits; miR-204-3p; oxidative stress; synaptic dysfunction.
Copyright © 2020 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Overexpression of miR-132-3p contributes to neuronal protection in in vitro and in vivo models of Alzheimer's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Jan 24;417:113584. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113584. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34536429
-
MicroRNA-574 is involved in cognitive impairment in 5-month-old APP/PS1 mice through regulation of neuritin.Brain Res. 2015 Nov 19;1627:177-88. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.09.022. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26423933
-
MiR-431 attenuates synaptic plasticity and memory deficits in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice.JCI Insight. 2023 Jun 22;8(12):e166270. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.166270. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37192007 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-455-5p/CPEB1 pathway mediates Aβ-related learning and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res Bull. 2021 Dec;177:282-294. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.10.008. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Brain Res Bull. 2021. PMID: 34678444 Review.
-
MicroRNA-455-3P as a peripheral biomarker and therapeutic target for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Sep;100:102459. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102459. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 39153602 Review.
Cited by
-
NOX4 exacerbates Parkinson's disease pathology by promoting neuronal ferroptosis and neuroinflammation.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jul 1;20(7):2038-2052. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01265. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38993139 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes and non-coding RNAs: bridging the gap in Alzheimer's pathogenesis and therapeutics.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Jan 4;40(1):84. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01520-7. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 39754674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recognizing Alzheimer's disease from perspective of oligodendrocytes: Phenomena or pathogenesis?CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Mar;30(3):e14688. doi: 10.1111/cns.14688. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38516808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progressive reduction of nuclear receptor Nr4a1 mediates age-dependent cognitive decline.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 May;20(5):3504-3524. doi: 10.1002/alz.13819. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 38605605 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADPH) Oxidase and Its Inhibitors in Alzheimer's Disease Murine Models.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 2;10(2):218. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020218. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33540840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association 2019 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2019;15:321–387.
-
- Zhang Y., Song W. Islet amyloid polypeptide: Another key molecule in Alzheimer’s pathogenesis? Prog. Neurobiol. 2017;153:100–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

