Drug retention, inactive disease and response rates in 1860 patients with axial spondyloarthritis initiating secukinumab treatment: routine care data from 13 registries in the EuroSpA collaboration
- PMID: 32950963
- PMCID: PMC7539854
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001280
Drug retention, inactive disease and response rates in 1860 patients with axial spondyloarthritis initiating secukinumab treatment: routine care data from 13 registries in the EuroSpA collaboration
Abstract
Objectives: To explore 6-month and 12-month secukinumab effectiveness in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) overall, as well as across (1) number of previous biologic/targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs), (2) time since diagnosis and (3) different European registries.
Methods: Real-life data from 13 European registries participating in the European Spondyloarthritis Research Collaboration Network were pooled. Kaplan-Meier with log-rank test, Cox regression, χ² and logistic regression analyses were performed to assess 6-month and 12-month secukinumab retention, inactive disease/low-disease-activity states (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) <2/<4, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) <1.3/<2.1) and response rates (BASDAI50, Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) 20/40, ASDAS clinically important improvement (ASDAS-CII) and ASDAS major improvement (ASDAS-MI)).
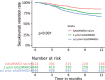
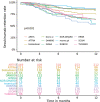
Results: We included 1860 patients initiating secukinumab as part of routine care. Overall 6-month/12-month secukinumab retention rates were 82%/72%, with significant (p<0.001) differences between the registries (6-month: 70-93%, 12-month: 53-86%) and across number of previous b/tsDMARDs (b/tsDMARD-naïve: 90%/73%, 1 prior b/tsDMARD: 83%/73%, ≥2 prior b/tsDMARDs: 78%/66%). Overall 6-month/12-month BASDAI<4 were observed in 51%/51%, ASDAS<1.3 in 9%/11%, BASDAI50 in 53%/47%, ASAS40 in 28%/22%, ASDAS-CII in 49%/46% and ASDAS-MI in 25%/26% of the patients. All rates differed significantly across number of previous b/tsDMARDs, were numerically higher for b/tsDMARD-naïve patients and varied significantly across registries. Overall, time since diagnosis was not associated with secukinumab effectiveness.
Conclusions: In this study of 1860 patients from 13 European countries, we present the first comprehensive real-life data on effectiveness of secukinumab in patients with axSpA. Overall, secukinumab retention rates after 6 and 12 months of treatment were high. Secukinumab effectiveness was consistently better for bionaïve patients, independent of time since diagnosis and differed across the European countries.
Keywords: DMARDs (biologic); Outcomes research; Spondyloarthritis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: BM: consultancy fees and research grant from Novartis. UL: None. CC: None. AC: fees for speaking and/or consulting from AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen-Cilag, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB. JZ: none. AGL: research grant from Novartis, consultant for/served on the speakers bureau for AbbVie, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. MP-S: speaker and consultancy fees from Abbvie, BMS, Janssen, Lilly, MSD and Sanofi. FO: speaker and consultancy fees from Abbvie, Abdi Ibrahim, Amgen, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and UCB and research grant from Pfizer. TKK: fees for speaking and/or consulting from AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celltrion, Egis, Eli Lilly, Hikma, MSD, Mylan, Novartis/Sandoz, Oktal, Orion Pharma, Hospira/Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and UCB and received research funding to Diakonhjemmet Hospital from AbbVie, BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Roche and UCB. ZR: speaker and consultancy fees from Abbvie, Amgen, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Medis, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi. MJS: speaker fees from Novartis and Pfizer. FI: speaker and consulting fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, UCB, MSD. AMH: research grant from MSD. BG: Speaker fee from Novartis. JA: none. RI: consulting fees from Abbvie, Eli-Lilly, Ewopharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz. MJN: fees for speaking and/or consulting from AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Novartis and Pfizer. KP: honoraria for lectures from MSD, BMS, AbbVie, UCB, Roche, Biogen, Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, Medac, Egis. CS-P: none. SA: has received grant/research support from, been a consultant for, and served on the speakers bureau for AbbVie, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. JS: none. MT: none. HS: speaker fees from Novartis, Pfizer and Abbvie. MS: none. JÖ: none. AjG: None. GM: none. IvdH-B: Fees for speaking and/or consulting from Abbvie, Lilly, Novartis, BMS, MSD, UCB and Pfizer. SG: none. CHB: research grant from Novartis. LØ: research grant from Novartis. MH: grant from AbbVie, Biogen, BMS, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB. Personal fee from CellTrion, MSD, Orion, Samsung. MO: consultancy fees and/or speaker fees form Abbvie, BMS, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Hospira, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Novo, Orion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi and UCB; and research support from Abbvie, BMS, Celgene, Merck, and Novartis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatment response and drug retention rates in 24 195 biologic-naïve patients with axial spondyloarthritis initiating TNFi treatment: routine care data from 12 registries in the EuroSpA collaboration.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Nov;78(11):1536-1544. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215427. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 31431486
-
Four-year secukinumab treatment outcomes in European real-world patients with axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2025 May;92(3):105824. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2024.105824. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Joint Bone Spine. 2025. PMID: 39608666
-
Predictors of Secukinumab Treatment Response and Continuation in Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results From the EuroSpA Research Collaboration Network.J Rheumatol. 2025 Jun 1;52(6):572-582. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2024-0920. J Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39892891
-
Comparison of Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index tools in assessment of axial spondyloarthritis activity.Reumatologia. 2024;62(1):64-69. doi: 10.5114/reum/185429. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Reumatologia. 2024. PMID: 38558891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs targeting remission in axial spondyloarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Nov 1;59(11):3158-3171. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa268. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 32696064
Cited by
-
Using natural language processing to explore characteristics and management of patients with axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis treated under real-world conditions in Spain: SpAINET study.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2023 Dec 24;15:1759720X231220818. doi: 10.1177/1759720X231220818. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2023. PMID: 38146537 Free PMC article.
-
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Reshape the Future-From the "2022 GISEA International Symposium".J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 19;11(24):7537. doi: 10.3390/jcm11247537. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36556152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secukinumab in axial spondyloarthritis: a narrative review of clinical evidence.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021 Aug 28;13:1759720X211041854. doi: 10.1177/1759720X211041854. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021. PMID: 34471428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secukinumab May Be an Effective Treatment Option for Axial Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis Patients with a History of Malignancy: Multicenter Real-Life Experience from Turkey.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 18;13(20):6216. doi: 10.3390/jcm13206216. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39458166 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-IL-17 Agents in the Treatment of Axial Spondyloarthritis.Immunotargets Ther. 2021 May 3;10:141-153. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S259126. eCollection 2021. Immunotargets Ther. 2021. PMID: 33977094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
