Semaphorins or Frizzled -it is the receptor that direct the action of clostridial glucosylating toxins
- PMID: 32951001
- PMCID: PMC7502071
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-00307-3
Semaphorins or Frizzled -it is the receptor that direct the action of clostridial glucosylating toxins
Figures
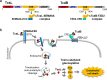
Comment on
-
Recognition of Semaphorin Proteins by P. sordellii Lethal Toxin Reveals Principles of Receptor Specificity in Clostridial Toxins.Cell. 2020 Jul 23;182(2):345-356.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.005. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32589945 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

