Relation of Helicobacter pylori infection to peripheral arterial stiffness and 10-year cardiovascular risk in subjects with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 32951444
- PMCID: PMC7919201
- DOI: 10.1177/1479164120953626
Relation of Helicobacter pylori infection to peripheral arterial stiffness and 10-year cardiovascular risk in subjects with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Purpose: This study was conducted to investigate the relation of HP infection to peripheral arterial stiffness and 10-year cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus (DM).
Methods: DM subjects who underwent the C13-breath test were enrolled and divided into DMHP+ and DMHP- groups. Peripheral arterial stiffness was measured using brachial to ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV). Framingham score (FRS) and Chinese evaluation method of ischemic cardiovascular diseases (ICVD) were used to clarify 10-year cardiovascular risk.
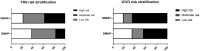
Results: A total of 6767 subjects were included, baPWV and proportion of subjects with severe peripheral arterial stiffness were lower in DMHP- group than DMHP+ group (1556.68 ± 227.54 vs 2031.61 ± 525.48 cm/s, p < 0.01; 21.9% vs 62.7%, p < 0.01). Multivariate logistic regression analysis demonstrated that HP infection was independently associated with baPWV. Furthermore, cardiovascular risk score and the proportion of subjects with high risk were lower in DMHP- group than DMHP+ group (FRS: 12.09 ± 3.77 vs 13.91 ± 3.77, 17.2% vs 38.8%; ICVD: 8.56 ± 2.99 vs 10.22 ± 3.16, 43.9% vs 65.4%, with all p < 0.05).
Conclusion: DM subjects with HP infection had more severe peripheral arterial stiffness compared those without HP infection, a higher cardiovascular risk score and 10-year cardiovascular risk stratification were observed in those subjects.
Keywords: Chinese ICVD; Diabetes mellitus; Framingham score; Helicobacter pylori; peripheral arterial stiffness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Balakumar P, Maung-UK, Jagadeesh G. Prevalence and prevention of cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus. Pharmacol Res 2016; 113: 600–609. - PubMed
-
- Wan Z, Hu L, Hu M, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and prevalence of high blood pressure among Chinese adults. J Hum Hypertens 2018; 32(2): 158–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous