Ultrasensitive supersandwich-type electrochemical sensor for SARS-CoV-2 from the infected COVID-19 patients using a smartphone
- PMID: 32952300
- PMCID: PMC7489230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.128899
Ultrasensitive supersandwich-type electrochemical sensor for SARS-CoV-2 from the infected COVID-19 patients using a smartphone
Abstract
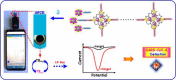
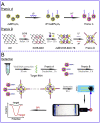
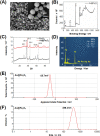
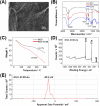
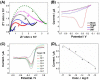
The recent pandemic outbreak of COVID-19 caused by a novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), poses a threat to public health globally. Thus, developing a rapid, accurate, and easy-to-implement diagnostic system for SARS-CoV-2 is crucial for controlling infection sources and monitoring illness progression. Here, we reported an ultrasensitive electrochemical detection technology using calixarene functionalized graphene oxide for targeting RNA of SARS-CoV-2. Based on a supersandwich-type recognition strategy, the technology was confirmed to practicably detect the RNA of SARS-CoV-2 without nucleic acid amplification and reverse-transcription by using a portable electrochemical smartphone. The biosensor showed high specificity and selectivity during in silico analysis and actual testing. A total of 88 RNA extracts from 25 SARS-CoV-2-confirmed patients and eight recovery patients were detected using the biosensor. The detectable ratios (85.5 % and 46.2 %) were higher than those obtained using RT-qPCR (56.5 % and 7.7 %). The limit of detection (LOD) of the clinical specimen was 200 copies/mL, which is the lowest LOD among the published RNA measurement of SARS-CoV-2 to date. Additionally, only two copies (10 μL) of SARS-CoV-2 were required for per assay. Therefore, we developed an ultrasensitive, accurate, and convenient assay for SARS-CoV-2 detection, providing a potential method for point-of-care testing.
Keywords: Calixarene; Electrochemical biosensor; SARS-CoV-2; Smartphone; Supersandwich-type biosensor.
© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid, Ultrasensitive, and Quantitative Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Antisense Oligonucleotides Directed Electrochemical Biosensor Chip.ACS Nano. 2020 Dec 22;14(12):17028-17045. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c06392. Epub 2020 Oct 20. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 33079516
-
Rapid and Visual Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Multiplex Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Linked With Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jul 14;11:581239. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.581239. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34336708 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Clinical Application of a Rapid and Sensitive Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Test for SARS-CoV-2 Infection.mSphere. 2020 Aug 26;5(4):e00808-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00808-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32848011 Free PMC article.
-
Graphene-based biosensors for detecting coronavirus: a brief review.Nanoscale. 2023 Nov 23;15(45):18184-18197. doi: 10.1039/d3nr04583h. Nanoscale. 2023. PMID: 37927083 Review.
-
Clinical Utility of Biosensing Platforms for Confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 May 24;11(6):167. doi: 10.3390/bios11060167. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peptide-based direct electrochemical detection of receptor binding domains of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in pristine samples.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2023 Feb 15;377:133052. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2022.133052. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2023. PMID: 36438197 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in airborne pathogen detection using optical and electrochemical biosensors.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 Nov 22;1234:340297. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.340297. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 36328717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 diagnostics: Molecular biology to nanomaterials.Clin Chim Acta. 2023 Jan 1;538:139-156. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2022.11.017. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Clin Chim Acta. 2023. PMID: 36403665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amperometric immunosensor developed for sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike S1 protein in combined with portable device.Talanta. 2022 Jul 1;244:123422. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123422. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Talanta. 2022. PMID: 35395458 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the recent achievements on coronaviruses recognition using electrochemical detection methods.Microchem J. 2022 Jul;178:107322. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2022.107322. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Microchem J. 2022. PMID: 35233118 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Web reference 1: WHO Timeline-COVID-19, https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/detail/27-04-2020-who-timeline-covid-19 (accessed 2020/04/27).
-
- Web reference 2: COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic, https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/(accessed 2020/09/04).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

