Comparison of Involved Field Radiotherapy versus Elective Nodal Irradiation in Stage IIIB/C Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma Patients Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy: A Propensity Score Matching Study
- PMID: 32952557
- PMCID: PMC7487114
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7083149
Comparison of Involved Field Radiotherapy versus Elective Nodal Irradiation in Stage IIIB/C Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma Patients Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy: A Propensity Score Matching Study
Abstract
Background: We retrospectively compared the incidence of isolated elective nodal failure (IENF) and toxicity rates and survival outcomes after elective nodal irradiation (ENI) versus involved-field RT (IFRT) by employing the propensity score matching (PSM) methodology in stage IIIB/C inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with definitive concurrent chemoradiotherapy (C-CRT).
Methods: Our PSM examination included 1048 stage IIIB/C NSCLC patients treated with C-CRT from January 2007 to December 2016: a total dose of 66 Gy (2 Gy/fraction) radiotherapy and 1-3 cycles of platinum-based doublet chemotherapy concurrently. The primary and secondary endpoints were the IENF and toxicity rates and survival outcomes after ENI versus IFRT, respectively. Propensity scores were calculated for each group to adjust for confounding variables and facilitate well-balanced comparability by creating 1 : 1 matched study groups.
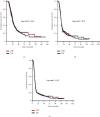
Results: The median follow-up was 26.4 months for the whole study accomplice. The PSM analysis unveiled 1 : 1 matched 646 patients for the ENI (N = 323) and IFRT (N = 323) cohorts. Intergroup comparisons discovered that the 5-year isolated ENF incidence rates (3.4% versus 4.3%; P=0.52) and median overall survival (25.2 versus 24.6 months; P=0.69), locoregional progression-free survival (15.3 versus 15.1 months; P=0.52), and progression-free survival (11.7 versus 11.2 months; P=0.57) durations were similar between the ENI and IFRT cohorts, separately. However, acute grade 3-4 leukopenia (P=0.0012), grade 3 nausea-vomiting (P=0.006), esophagitis (P=0.003), pneumonitis (P=0.002), late grade 3-4 esophageal toxicity (P=0.038), and the need for hospitalization (P < 0.001) were all significantly higher in the ENI than in the IFRT group, respectively.
Conclusion: Results of the present large-scale PSM cohort established the absence of meaningful IENF or survival differences between the IFRT and ENI cohorts and, consequently, counseled the IFRT as the elected RT technique for such patients since ENI increased the toxicity rates.
Copyright © 2020 Erkan Topkan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involved-field radiotherapy (IFRT) versus elective nodal irradiation (ENI) in combination with concurrent chemotherapy for 239 esophageal cancers: a single institutional retrospective study.Radiat Oncol. 2015 Aug 14;10:171. doi: 10.1186/s13014-015-0482-9. Radiat Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26269033 Free PMC article.
-
Elective nodal irradiation (ENI) vs. involved field radiotherapy (IFRT) for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A comparative analysis of toxicities and clinical outcomes.Radiother Oncol. 2010 May;95(2):178-84. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.02.007. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Radiother Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20356642
-
Elective nodal irradiation versus involved-field irradiation for stage II-IV cervical esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients undergoing definitive concurrent chemoradiotherapy: a retrospective propensity study with 8-year survival outcomes.Radiat Oncol. 2023 Aug 28;18(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02332-2. Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37641149 Free PMC article.
-
Involved field radiotherapy (IFRT) versus elective nodal irradiation (ENI) for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of incidence of elective nodal failure (ENF).Radiat Oncol. 2016 Sep 21;11(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0698-3. Radiat Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27655339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of involved field irradiation versus elective nodal irradiation in definitive radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer- a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 2;12:1034656. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1034656. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36408184 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Could elective nodal irradiation for locally advanced rectal cancer be omitted in the context of total neoadjuvant therapy? An analysis of the recurrence sites of rectal cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Nov 27;14:1459024. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1459024. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39664184 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of digital positron emission tomography/computed tomography on the delineation of clinical target volume in advanced lung cancer.Mol Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov 6;19(6):102. doi: 10.3892/mco.2023.2698. eCollection 2023 Dec. Mol Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38022846 Free PMC article.
-
<Editors' Choice> Elective nodal irradiation versus involved field radiotherapy for limited disease small cell lung cancer: a single-institution experience.Nagoya J Med Sci. 2022 May;84(2):327-338. doi: 10.18999/nagjms.84.2.327. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35967948 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Impact of Supraclavicular Lymph Node Involvement of Stage IIIC Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Mar 23;57(3):301. doi: 10.3390/medicina57030301. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 33807016 Free PMC article.
-
Joint EANM/SNMMI/ESTRO practice recommendations for the use of 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT external beam radiation treatment planning in lung cancer V1.0.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Mar;49(4):1386-1406. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05624-5. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35022844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Furuse K., Fukuoka M., Kawahara M., et al. Phase III study of concurrent versus sequential thoracic radiotherapy in combination with mitomycin, vindesine, and cisplatin in unresectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1999;17(9):2692–2699. doi: 10.1200/jco.1999.17.9.2692. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Belderbos J. S. A., Kepka L., Kong F.-M., Martel M. K., Videtic G. M. M., Jeremic B. Report from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) consultants’ meeting on elective nodal irradiation in lung cancer: non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) International Journal of Radiation Oncology∗Biology∗Physics. 2008;72(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.04.081. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous