Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Modulates RhoA/ROCK Signaling of Rat Mandibular Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Rescue Their Damaged Cytoskeletal Organization and Cell Biological Function Induced by Radiation
- PMID: 32952571
- PMCID: PMC7482001
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8863577
Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Modulates RhoA/ROCK Signaling of Rat Mandibular Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Rescue Their Damaged Cytoskeletal Organization and Cell Biological Function Induced by Radiation
Abstract
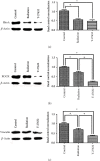
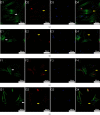
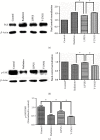
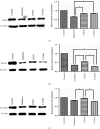
Osteoradionecrosis of the jaw (ORNJ) is an infrequent yet potentially devastating complication of head and neck radiation therapy. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) has been widely accepted as a promising method for the successful management of ORNJ, but the mechanism remains unclear. In this study, the effects of LIPUS on cytoskeletal reorganization, cell viability, and osteogenic differentiation capacity of rat mandible-derived bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (M-BMMSCs) induced by radiation were determined by immunofluorescence staining, CCK-8 cell proliferation assay, quantification of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, alizarin red staining, and real-time RT-PCR, respectively. Moreover, the involvement of the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway underlying this process was investigated via western blot analysis. We found that radiation induced significant damage to the cytoskeleton, cell viability, and osteogenic differentiation capacity of M-BMMSCs and downregulated their expression of RhoA, ROCK, and vinculin while increasing FAK expression. LIPUS treatment effectively rescued the disordered cytoskeleton and redistributed vinculin. Furthermore, the cell viability and osteogenic differentiation capacity were also significantly recovered. More importantly, it could reverse the aberrant expression of the key molecules induced by radiation. Inhibition of RhoA/ROCK signaling remarkably aggravated the inhibitory effect of radiation and attenuated the therapeutic effect of LIPUS. In the light of these findings, the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway might be a promising target for modifying the therapeutic effect of LIPUS on osteoradionecrosis.
Copyright © 2020 Rong Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LIPUS inhibited the expression of inflammatory factors and promoted the osteogenic differentiation capacity of hPDLCs by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway.J Periodontal Res. 2020 Jan;55(1):125-140. doi: 10.1111/jre.12696. Epub 2019 Sep 21. J Periodontal Res. 2020. PMID: 31541455
-
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound reduces alveolar bone resorption during orthodontic treatment via Lamin A/C-Yes-associated protein axis in stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2024 Mar 26;16(3):267-286. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i3.267. World J Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 38577236 Free PMC article.
-
[Regulation of cell deformation induced by RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway in osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Jan 15;99(3):212-217. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2019.03.012. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30669766 Chinese.
-
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound regulates osteoblast-osteoclast crosstalk via EphrinB2/EphB4 signaling for orthodontic alveolar bone remodeling.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jun 23;11:1192720. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1192720. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37425367 Free PMC article.
-
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation facilitates in vitro osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells via up-regulation of heat shock protein (HSP)70, HSP90, and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway.Biosci Rep. 2018 May 22;38(3):BSR20180087. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180087. Print 2018 May 29. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29789443 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Static Magnetic Fields Enhance the Chondrogenesis of Mandibular Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Coculture Systems.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Nov 27;2021:9962861. doi: 10.1155/2021/9962861. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34873576 Free PMC article.
-
[Lycium barbarum glycopeptide reduces bone loss caused by exosomes derived from human gingival fibroblasts with radiation exposure].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Sep 20;44(9):1752-1759. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.15. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39505343 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Latest progress in low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for studying exosomes derived from stem/progenitor cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 28;14:1286900. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1286900. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38089611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful Management of Radiation-Associated Insufficiency Fracture of the Tibial Plateau with Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound.Am J Case Rep. 2022 Jan 15;23:e934372. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.934372. Am J Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35031593 Free PMC article.
-
Chidamide inhibits cell glycolysis in acute myeloid leukemia by decreasing N6-methyladenosine-related GNAS-AS1.Daru. 2024 Jun;32(1):11-24. doi: 10.1007/s40199-023-00482-y. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Daru. 2024. PMID: 37926762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel V., Gadiwalla Y., Sassoon I., Sproat C., Kwok J., McGurk M. Prophylactic use of pentoxifylline and tocopherol in patients who require dental extractions after radiotherapy for cancer of the head and neck. The British Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery. 2016;54(5):547–550. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2016.02.024. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

