Approach to Patients with Neurometabolic Diseases Who Show Characteristic Signs and Symptoms
- PMID: 32952579
- PMCID: PMC7468080
Approach to Patients with Neurometabolic Diseases Who Show Characteristic Signs and Symptoms
Abstract
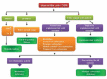
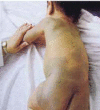
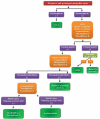
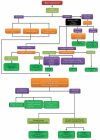
Neurometabolic disorders are hereditary conditions mainly affect the function of the brain and the nervous system. The prevalence of these disorders is 1 in 1,000 live births. Such disorders, at different ages, could manifest as sepsis, hypoglycemia, and other neurologic disorders. Having similar manifestations leads to delayed diagnosis of neurometabolic disorders. A number of neurometabolic disorders have known treatments; however, to prevent long-term complications the key factors are early diagnosis and treatment. Although a large number of neurometabolic diseases have no treatment or cure, the correct and on-time diagnosis before death is important for parents to have plans for prenatal diagnosis. Different diagnostic procedures could be offered to parents, enzymatic procedures, and determining metabolites in plasma, urine, and CSF, and molecular genetic diagnosis. Molecular genetic diagnostic procedures are expensive and could not be offered to all parents. Therefore, we aimed to design algorithms to diagnose neurometabolic disorders according to some frequent and characteristic signs and symptoms. By designing these algorithms and using them properly, we could offer diagnostic enzymatic panels. These enzymatic panels are inexpensive; thereby reducing the financial burden on the parents. Also, having an early diagnosis according to these panels could lead to offering more accurate and less expensive molecular genetic tests.
Keywords: Neurometabolic disorders; algorithms; children; diagnosis; enzymatic panels.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hereditary neurometabolic causes of infantile spasms in 80 children presenting to a tertiary care center.Pediatr Neurol. 2014 Sep;51(3):390-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.05.015. Epub 2014 May 21. Pediatr Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25160544
-
Diagnostic approach in adult-onset neurometabolic diseases.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2022 Apr;93(4):413-421. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2021-328045. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35140137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Approach to neurometabolic diseases from a pediatric neurological point of view.Iran J Child Neurol. 2015 Winter;9(1):1-16. Iran J Child Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25767534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eye motor manifestations in children with neurometabolic disorders.J Formos Med Assoc. 2022 Apr;121(4):736-748. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2021.09.003. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Formos Med Assoc. 2022. PMID: 34561118 Review.
-
Neurometabolic Diagnosis in Children who referred as Neurodevelopmental Delay (A Practical Criteria, in Iranian Pediatric Patients).Iran J Child Neurol. 2016 Summer;10(3):73-81. Iran J Child Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27375759 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2-Related Factor 2 Signaling in the Neuropathophysiology of Inherited Metabolic Disorders.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Nov 26;15:785057. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.785057. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34955754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and clinical translation of ex vivo gene therapy.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun 11;20:2986-3003. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.015. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35782737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Filiano JJ. Neurometabolic diseases in the newborn. Clin Perinatol. 2006;33(2):411–79. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes Filho JA, Shapiro BE. Tay-Sachs disease. Arch Neurol. 2004;61(9):1466–8. - PubMed
-
- Suvarna JC, Hajela SA. Cherry-red spot. J Postgrad Med. 2008;54(1):54–7. - PubMed
-
- Gieselmann V, Franken S, Klein D, Mansson JE, Sandhoff R, Lullmann Rauch R, et al. Metachromatic leukodystrophy: consequences of sulphatide accumulation. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 2003;92(443):74–9; discussion 45. - PubMed
-
- Dierks T, Schlotawa L, Frese MA, Radhakrishnan K, von Figura K, Schmidt B. Molecular basis of multiple sulfatase deficiency, mucolipidosis II/III and Niemann-Pick C1 disease - Lysosomal storage disorders caused by defects of non-lysosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1793(4):710–25. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
