Engineered targeting tLyp-1 exosomes as gene therapy vectors for efficient delivery of siRNA into lung cancer cells
- PMID: 32952669
- PMCID: PMC7486479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2019.04.002
Engineered targeting tLyp-1 exosomes as gene therapy vectors for efficient delivery of siRNA into lung cancer cells
Abstract
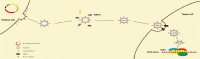
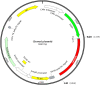
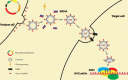
Natural exosomes can express specific proteins and carbohydrate molecules on the surface and hence have demonstrated the great potentials for gene therapy of cancer. However, the use of natural exosomes is restricted by their low transfection efficiency. Here, we report a novel targeting tLyp-1 exosome by gene recombinant engineering for delivery of siRNA to cancer and cancer stem cells. To reach such a purpose, the engineered tLyp-1-lamp2b plasmids were constructed and amplified in Escherichia coli. The tLyp-1-lamp2b plasmids were further used to transfect HEK293T tool cells and the targeting tLyp-1 exosomes were isolated from secretion of the transfected HEK293T cells. Afterwards, the artificially synthesized siRNA was encapsulated into targeting tLyp-1 exosomes by electroporation technology. Finally, the targeting siRNA tLyp-1 exosomes were used to transfect cancer or cancer stem cells. Results showed that the engineered targeting tLyp-1 exosomes had a nanosized structure (approximately 100 nm) and high transfection efficiency into lung cancer and cancer stem cells. The function verifications demonstrated that the targeting siRNA tLyp-1 exosomes were able to knock-down the target gene of cancer cells and to reduce the stemness of cancer stem cells. In conclusion, the targeting tLyp-1 exosomes are successfully engineered, and can be used for gene therapy with a high transfection efficiency. Therefore, the engineered targeting tLyp-1 exosomes offer a promising gene delivery platform for future cancer therapy.
Keywords: Engineering; Gene therapy; Lung cancer; Targeting tLyp-1exosomes; Transfection.
© 2019 Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Targeted Delivery of Exosomes Armed with Anti-Cancer Therapeutics.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;12(1):85. doi: 10.3390/membranes12010085. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35054611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered Exosomes for Targeted Transfer of siRNA to HER2 Positive Breast Cancer Cells.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019 Jan;187(1):352-364. doi: 10.1007/s12010-018-2813-4. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 29951961
-
Peptide-Targeted High-Density Lipoprotein Nanoparticles for Combinatorial Treatment against Metastatic Breast Cancer.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Aug 4;13(30):35248-35265. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c02074. Epub 2021 Jul 20. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 34284582
-
Exosomes of Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a Proper Vehicle for Transfecting miR-145 into the Breast Cancer Cell Line and Its Effect on Metastasis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jun 29;2021:5516078. doi: 10.1155/2021/5516078. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34307654 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome as a Natural Gene Delivery Vector for Cancer Treatment.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020;20(11):821-830. doi: 10.2174/1568009620666200924154149. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32972340 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered extracellular vesicles: A new approach for targeted therapy of tumors and overcoming drug resistance.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2024 Feb;44(2):205-225. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12518. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38155418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: Insights and therapeutic applications in cancer.Transl Oncol. 2022 Jul;21:101439. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101439. Epub 2022 May 9. Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35551002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Delivery of Exosomes Armed with Anti-Cancer Therapeutics.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;12(1):85. doi: 10.3390/membranes12010085. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35054611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling Novel Avenues in mTOR-Targeted Therapeutics: Advancements in Glioblastoma Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 6;24(19):14960. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914960. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Therapy: Non-Viral Delivery and Stimuli-Responsive Nanoformulations.Molecules. 2025 Jan 24;30(3):542. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030542. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Travis W.D., Brambilla E., Noguchi M., Nicholson A.G., Geisinger K.R., Yatabe Y. International association for the study of lung cancer/American thoracic society/European respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6(2):244–285. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mulligan R.C. The basic science of gene therapy. Science. 1993;260(5110):926–932. - PubMed
-
- Eugene H., Kaji E.H., Leiden J.M. Gene and stem cell therapies. JAMA. 2001;285(5):545–550. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

