Ultrasound-Guided Versus Anatomic Landmark-Guided Steroid Injection of the Subacromial Bursa in the Management of Subacromial Impingement: A Systematic Review of Randomised Control Studies
- PMID: 32952904
- PMCID: PMC7474019
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-020-00148-w
Ultrasound-Guided Versus Anatomic Landmark-Guided Steroid Injection of the Subacromial Bursa in the Management of Subacromial Impingement: A Systematic Review of Randomised Control Studies
Abstract
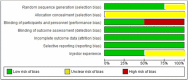
This study is a systematic review of prospective randomised control studies comparing ultrasound-guided steroid injection of the subacromial space with anatomic landmark-guided injection in the treatment of subacromial impingement to determine if there is any difference in pain relief and functional outcome. Mesh terms and free-text words search of electronic databases, reference list of identified studies and grey literature was performed using the PICO format. All identified papers were sifted sequentially by title, abstract and review of full text articles. Four papers qualified and were included in the review and analysis. The total number of patients in the studies was 234 patients with 117 patients randomised to each of landmark-guided and ultrasound-guided injection groups. There was no statistically significant difference in VAS pain scores (P = 0.67), SDQ scores (P = 0.43), SPADI disability score (P = 0.17) and functional outcomes scores (P = 0.09) at 4 to 6 weeks when USS-guided subacromial steroid injection was compared with landmark-guided injection. SPADI pain scores (P = 0.02) demonstrates significant reduction in favour of landmark-guided injection. There was low to moderate risk of bias. In conclusion, ultrasound-guided subacromial steroid injection does not offer any statistically significant clinical improvement over landmark-guided injection in adults with subacromial impingement.
Keywords: Anatomic landmark guided injection; Steroid injection; Subacromial bursitis; Subacromial impingement; Ultrasound guided injection.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Versus Anatomic Landmark-Guided Corticosteroid Injection on Pain, Physical Function, and Safety in Patients With Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2022 Dec 1;101(12):1087-1098. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000001940. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2022. PMID: 34966059 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the Critical Shoulder Angle on the Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Steroid Injection for Subacromial Bursitis.J Pers Med. 2022 Nov 9;12(11):1879. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111879. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36579587 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound guided versus landmark guided corticosteroid injection in patients with rotator cuff syndrome: Randomised controlled trial.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018 Mar;9(Suppl 1):S80-S85. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Feb 7. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018. PMID: 29628705 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of placement of ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection for subacromial pain (impingement) syndrome does not influence pain and function: Secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial.Musculoskeletal Care. 2022 Dec;20(4):831-838. doi: 10.1002/msc.1634. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Musculoskeletal Care. 2022. PMID: 35316556 Clinical Trial.
-
Needle placement approach to subacromial injection in patients with subacromial impingement syndrome: A systematic review.Musculoskeletal Care. 2019 Mar;17(1):13-22. doi: 10.1002/msc.1375. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Musculoskeletal Care. 2019. PMID: 30623595
Cited by
-
(4-Aminopyridine)-PLGA-PEG as a Novel Thermosensitive and Locally Injectable Treatment for Acute Peripheral Nerve Injury.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021 May 17;4(5):4140-4151. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c01566. Epub 2021 Apr 19. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021. PMID: 34142019 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of ultrasound- vs. landmark-guided injections for musculoskeletal pain: an umbrella review.J Rehabil Med. 2024 Aug 26;56:jrm40679. doi: 10.2340/jrm.v56.40769. J Rehabil Med. 2024. PMID: 39185547 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Injections in Patients Unable to Access or Benefit From Physical Therapy: A Comparative Study of Subacromial Corticosteroid Injection, Suprascapular Nerve Block, and Their Combination in Shoulder Impingement Syndrome.Cureus. 2025 Feb 14;17(2):e79008. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79008. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40091925 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-guided versus blind arthrocentesis in knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jan 31;104(5):e41389. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041389. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39889185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strakowski JA, Wiand W, Johnson EW. Upper limb musculoskeletal pain syndromes. In: Bradom RL, editor. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 3. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2000. pp. 792–817.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
