L-Carnitine potentiates the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of diclofenac sodium in an experimentally-induced knee osteoarthritis rat model
- PMID: 32952950
- PMCID: PMC7478254
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.43136.10138
L-Carnitine potentiates the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of diclofenac sodium in an experimentally-induced knee osteoarthritis rat model
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of the present research is to investigate the efficacy of L-carnitine (LC) as a complementary therapy to diclofenac sodium (Dic) treatment in a mono-iodoacetate (MIA) induced knee osteoarthritis (OA) rat model, with respect to pain relief and the underlying pathology.
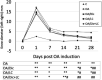
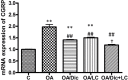
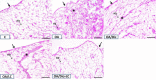
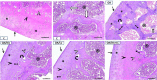
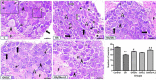
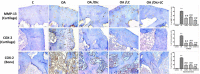
Materials and methods: Fifty adult male albino rats were randomly divided into five groups (n=10): Control, OA, OA/Dic, OA/LC, and OA/Dic+LC. Knee diameter and pain assessment tests were done weekly. After four weeks, serum malondialdehyde, reduced glutathione, interleukin 1-β, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, prostaglandin E2, and bone-specific alkaline phosphatase were measured. The injected knees were removed and processed for the histological and immunohistological study of matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2). Also, histological examination of dorsal root ganglia and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) expression in the spinal cord were assessed.
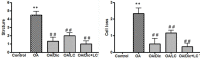
Results: Treatment with Dic and/or LC significantly reduced knee swelling, improved pain-related behaviors, inflammatory and oxidative stress markers, attenuated the MIA-mediated histopathological alteration in the knee joint, and down-regulated expression of MMP-13 and COX-2 in the knee joint. It, also, significantly reduced CGRP expression, compared with the OA group. Dic+LC showed a better effect in improving some parameters than each treatment alone.
Conclusion: LC plus Dic is a more effective therapy than Dic alone for OA treatment.
Keywords: CGRP; COX-2; L-carnitine; MMP-13; Osteoarthritis.
Figures


References
-
- Prince MJ, Wu F, Guo Y, Robledo LM, O’Donnell M, Sullivan R, et al. The burden of disease in older people and implications for health policy and practice. Lancet. 2015;385:549–562. - PubMed
-
- Feller AG, Rudman D. Role of carnitine in human nutrition. J Nutr. 1988;118:541–547. - PubMed
-
- Eteraf-Oskouei T, Ghasemoghli H, Najafi M. Effects of L-carnitine on inflammatory parameters and angiogenesis in the rat air pouch model of inflammation. J Isfahan Med School. 2017;35:807–813.
-
- Surai PF. Antioxidant action of carnitine: molecular mechanisms and practical applications. EC Vet Sci. 2015;2:66–84.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
