Social Support and Academic Achievement of Chinese Low-Income Children: A Mediation Effect of Academic Resilience
- PMID: 32952960
- PMCID: PMC7498124
- DOI: 10.21500/20112084.4480
Social Support and Academic Achievement of Chinese Low-Income Children: A Mediation Effect of Academic Resilience
Abstract
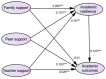
Using nation-wide survey data (N=2328) from China, this study investigates how social support from family, peers, and teachers influence low-income household children's (from 13 to 15 years old) academic resilience, as well as how academic resilience mediates the relationship between social support and children's academic achievement. Structural equation modelling was adopted to analyse the data. The results reveal that (1) low-income household children's family, peer, and teacher support are associated with their academic resilience; (2) peer support and academic resilience of low-income household children significantly relate with their academic achievements; (3) academic resilience plays a full mediation role in teacher support and a partial mediation role in peer support on children's academic achievement. The implications of this study on theory and practice, the limitations, and future research directions are discussed.
Utilizando datos de encuestas a nivel nacional (N = 2328) de China, este estudio investiga cómo el apoyo social de la familia, los compañeros y los maestros influyen en la resiliencia académica de los niños de bajos ingresos (de 13 a 15 años), así como la resiliencia académica interviene en la relación entre el apoyo social y el rendimiento académico de los niños. Se adoptó el modelo de ecuaciones estructurales para analizar los datos. Los resultados revelan que (1) el apoyo familiar, de pares y de maestros de niños de bajos ingresos en el hogar está asociado con su capacidad de resilencia académica; (2) el apoyo entre pares y la resilencia académica de los niños de hogares de bajos ingresos se relacionan significativamente con sus logros académicos; (3) la capacidad de resilencia académica desempeña un papel de mediación total en el apoyo del maestro y un papel de mediación parcial en el apoyo de los compañeros en el rendimiento académico de los niños. Se discuten las implicaciones de este estudio en la teoría y la práctica, además de las limitaciones y las futuras direcciones de investigación.
Keywords: Academic achievement; Academic resilience; Low-income children; Social support.
Similar articles
-
Family socio-economic status and children's academic achievement: The different roles of parental academic involvement and subjective social mobility.Br J Educ Psychol. 2020 Sep;90(3):561-579. doi: 10.1111/bjep.12374. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Br J Educ Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32777088
-
Effect of Self-Esteem and Parents' Psychological Control on the Relationship Between Teacher Support and Chinese Migrant Children's Academic Achievement: A Moderated Mediation.Front Psychol. 2019 Nov 1;10:2342. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02342. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31736816 Free PMC article.
-
Academic Resilience Despite Early Academic Adversity: A Three-Wave Longitudinal Study on Regulation-Related Resiliency, Interpersonal Relationships, and Achievement in First to Third Grade.Early Educ Dev. 2018;29(5):762-779. doi: 10.1080/10409289.2018.1429766. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Early Educ Dev. 2018. PMID: 30197488 Free PMC article.
-
Data on Singapore longitudinal early development study (SG-LEADS).Data Brief. 2024 Feb 17;53:110203. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2024.110203. eCollection 2024 Apr. Data Brief. 2024. PMID: 38419773 Free PMC article.
-
Children's Perspectives on Fairness and Inclusivity in the Classroom.Span J Psychol. 2022 Nov 2;25:e28. doi: 10.1017/SJP.2022.24. Span J Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36321422 Review.
Cited by
-
Teacher support and secondary school students' learning engagement: A moderated mediation model.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 23;15(1):2974. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87366-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39849054 Free PMC article.
-
ADHD Symptoms and Educational Level in Adolescents: The Role of the Family, Teachers, and Peers.Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2023 Jul;51(7):1051-1066. doi: 10.1007/s10802-023-01047-y. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2023. PMID: 36952076 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Teacher Resilience: Keys to Well-Being and Performance in Chilean Elementary Education.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Mar 2;15(3):292. doi: 10.3390/bs15030292. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150187 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived academic support and academic achievement among Ethiopian first-year university students: the serial mediating roles of academic motivation and resilience.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 22;16:1605550. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1605550. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40766005 Free PMC article.
-
Academic Performance and Resilience in Secondary Education Students.J Intell. 2025 May 16;13(5):56. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence13050056. J Intell. 2025. PMID: 40422656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan, J., McKenna, J., & Dominey, S. (2014). Degrees of resilience: Profiling psychological resilience and prospective academic achievement in university inductees. British Journal of Guidance & Counselling, 42 (1), 9-25. doi:10.1080/03069885.2013.793784.
- Allan J., McKenna J., Dominey S. Degrees of resilience: Profiling psychological resilience and prospective academic achievement in university inductees. British Journal of Guidance & Counselling. 2014;42(1):9–25. doi: 10.1080/03069885.2013.793784. - DOI
-
- Ayala, J., & Manzano, G. (2018). Academic performance of first-year university students: The influence of resilience and engagement. Higher Education Research & Development, 37 (7), 1321-1335. doi:10.1080/07294360.2018.1502258.
- Ayala J., Manzano G. Academic performance of first-year university students: The influence of resilience and engagement. Higher Education Research & Development. 2018;37(7):1321–1335. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2018.1502258. - DOI
-
- Bernstein, B. (1962). Social class, linguistic codes and grammatical elements. Language and Speech, 5 (4), 221-240. doi:10.1177/002383096200500405.
- Bernstein B. Social class, linguistic codes and grammatical elements. Language and Speech. 1962;5(4):221–240. doi: 10.1177/002383096200500405. - DOI
-
- Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- Bronfenbrenner U. The ecology of human development. Cambridge: Harvard University Press; 1979.
-
- Chin, W. (2010). How to write up and report PLS analyses. In V. Esposito, W.W. Chin, J. Henseler, & H. Wang (Eds.), Handbook of partial least squares: Concepts, methods and applications (pp. 655-690). Heidelberg, Dordrecht, London, New York: Springer.
- Chin W. How to write up and report PLS analyses. In: Esposito V, Chin W.W., Henseler J., Wang H., editors. Handbook of partial least squares: Concepts, methods and applications. Heidelberg, Dordrecht, London, New York: Springer; 2010. pp. 655–690.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources