Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analytics in m-Health: A Healthcare System Perspective
- PMID: 32952992
- PMCID: PMC7481991
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8894694
Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analytics in m-Health: A Healthcare System Perspective
Abstract
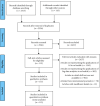
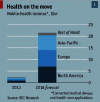
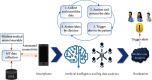
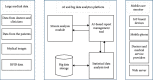
Mobile health (m-health) is the term of monitoring the health using mobile phones and patient monitoring devices etc. It has been often deemed as the substantial breakthrough in technology in this modern era. Recently, artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics have been applied within the m-health for providing an effective healthcare system. Various types of data such as electronic health records (EHRs), medical images, and complicated text which are diversified, poorly interpreted, and extensively unorganized have been used in the modern medical research. This is an important reason for the cause of various unorganized and unstructured datasets due to emergence of mobile applications along with the healthcare systems. In this paper, a systematic review is carried out on application of AI and the big data analytics to improve the m-health system. Various AI-based algorithms and frameworks of big data with respect to the source of data, techniques used, and the area of application are also discussed. This paper explores the applications of AI and big data analytics for providing insights to the users and enabling them to plan, using the resources especially for the specific challenges in m-health, and proposes a model based on the AI and big data analytics for m-health. Findings of this paper will guide the development of techniques using the combination of AI and the big data as source for handling m-health data more effectively.
Copyright © 2020 Z. Faizal khan and Sultan Refa Alotaibi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
m-Health 2.0: New perspectives on mobile health, machine learning and big data analytics.Methods. 2018 Dec 1;151:34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.05.015. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Methods. 2018. PMID: 29890285
-
Implications of Big Data Analytics, AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning in the Health Care System of Bangladesh: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Oct 28;26:e54710. doi: 10.2196/54710. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39466315 Free PMC article.
-
Towards an efficient and Energy-Aware mobile big health data architecture.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 Nov;166:137-154. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.10.008. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30415713
-
Big data analytics in medical engineering and healthcare: methods, advances and challenges.J Med Eng Technol. 2020 Aug;44(6):267-283. doi: 10.1080/03091902.2020.1769758. Epub 2020 Jun 5. J Med Eng Technol. 2020. PMID: 32498594 Review.
-
Opening the Black Box: Understanding the Science Behind Big Data and Predictive Analytics.Anesth Analg. 2018 Nov;127(5):1139-1143. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000003463. Anesth Analg. 2018. PMID: 29847384 Review.
Cited by
-
Utility of a Machine-Guided Tool for Assessing Risk Behavior Associated With Contracting HIV in Three Sites in South Africa: Protocol for an In-Field Evaluation.JMIR Res Protoc. 2021 Dec 2;10(12):e30304. doi: 10.2196/30304. JMIR Res Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34860679 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers to Dissemination of Local Health Data Faced by US State Agencies: Survey Study of Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Coordinators.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Jul 13;23(7):e16750. doi: 10.2196/16750. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34255650 Free PMC article.
-
Big Data-Based Epidemiology of Uveitis and Related Intraocular Inflammation.Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2021 Jan-Feb 01;10(1):60-62. doi: 10.1097/APO.0000000000000364. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2021. PMID: 33512828 Free PMC article.
-
Blockchain and artificial intelligence technology in e-Health.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Oct;28(38):52810-52831. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16223-0. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34476701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence in COVID-19 Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment and Management Decisions in China.J Med Syst. 2021 Jul 24;45(9):84. doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01757-0. J Med Syst. 2021. PMID: 34302549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sousa P. S., Sabugueiro D., Felizardo V., Couto R., Pires I., Garcia N. M. mHealth sensors and applications for personal aid. In: Adibi S., editor. Mobile Health. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2015. Springer Series in Bio-/Neuroinformatics vol 5.
-
- Darrell M. Improving health care through mobile medical devices and sensors. Brookings Institution Policy Report. 2013;10:1–13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

