The growth plate: a physiologic overview
- PMID: 32953135
- PMCID: PMC7484711
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190088
The growth plate: a physiologic overview
Abstract
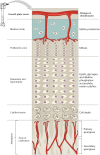
The growth plate is the cartilaginous portion of long bones where the longitudinal growth of the bone takes place. Its structure comprises chondrocytes suspended in a collagen matrix that go through several stages of maturation until they finally die, and are replaced by osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and lamellar bone.The process of endochondral ossification is coordinated by chondrocytes and a variety of humoral factors including growth hormone, parathyroid hormone, oestrogen, growth factors, cytokines, and various signalling pathways.Chondrocytes progress from a resting state to enter the phases of proliferation and hypertrophy. Under the influence of oestrogen, the proliferation of chondrocytes decreases as the resting chondrocytes are consumed. During the terminal phase of differentiation, cartilage is replaced by blood vessels and organized bone tissue, and once chondrocytes have died, the longitudinal growth of the bone ceases and the growth plate closes.The highly complex regulatory signals involved in this process are genetically determined, and genetic perturbations in any of the associated genes can result in abnormalities of bone growth. Hundreds of chondrodysplasias have been described, pointing to the complexity of the humoral control systems involved in endochondral ossification.While our knowledge of the mechanisms behind the various bone growth control systems is improving, a deeper understanding of the underlying processes could aid clinicians to better understand bone health and bone growth abnormalities. This review describes the current clinical research into the physiology of the growth plate. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2020;5:498-507. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190088.
Keywords: bone growth; chondrodysplasia; growth plate; physis.
© 2020 The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of interest statement: The author was granted a scholarship by the The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBİTAK) for travel and registration expenses for participation with an accepted oral presentation in the 38th SICOT Orthopaedic World Congress that was held in Cape Town, not related to the submitted work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Endochondral ossification: how cartilage is converted into bone in the developing skeleton.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(1):46-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.06.009. Epub 2007 Jun 29. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 17659995 Review.
-
The skeleton: a multi-functional complex organ: the growth plate chondrocyte and endochondral ossification.J Endocrinol. 2011 Nov;211(2):109-21. doi: 10.1530/JOE-11-0048. Epub 2011 Jun 3. J Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21642379 Review.
-
Expression of bone-specific genes by hypertrophic chondrocytes: implication of the complex functions of the hypertrophic chondrocyte during endochondral bone development.J Cell Biochem. 1996 Jul;62(1):1-9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(199607)62:1%3C1::AID-JCB1%3E3.0.CO;2-X. J Cell Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8836870 Review.
-
Interaction of growth factors regulating chondrocyte differentiation in the developing embryo.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9 Suppl A:S109-17. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001. PMID: 11680674 Review.
-
The chondrocytic journey in endochondral bone growth and skeletal dysplasia.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2014 Mar;102(1):52-73. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.21060. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2014. PMID: 24677723 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Saliva Composition: Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein, Total Protein, and Secretory Immunoglobulin A (sIgA) in Rattus norvegicus with Stunted Growth.Eur J Dent. 2023 Jul;17(3):765-770. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1755558. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Eur J Dent. 2023. PMID: 36220123 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of FGF-2, FGF-18 and Transcription Factor Activity by Perlecan in the Maturational Development of Transitional Rudiment and Growth Plate Cartilages and in the Maintenance of Permanent Cartilage Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 9;23(4):1934. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041934. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two cases of autosomal dominant familial short stature associated with COL11A2 gene variant and the therapeutic response to recombinant human growth hormone.Transl Pediatr. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):618-627. doi: 10.21037/tp-2024-551. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Transl Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40386356 Free PMC article.
-
Mineral Content and Extracellular Matrix Protein Expression in Mouse Growth Plates During Epiphyseal Fusion: An Observational Study.Calcif Tissue Int. 2025 Jun 6;116(1):81. doi: 10.1007/s00223-025-01391-9. Calcif Tissue Int. 2025. PMID: 40478277 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of biological stimuli and flexion induce microcavities promote hypertrophy and inhibit chondrogenesis during in vitro culture of human mesenchymal stem cell aggregates.Biotechnol J. 2024 Sep;19(9):e2400060. doi: 10.1002/biot.202400060. Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39295570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nilsson O, Marino R, De Luca F, Phillip M, Baron J. Endocrine regulation of the growth plate. Horm Res 2005;64:157–165. - PubMed
-
- Jaroszewicz J, Kosowska A, Hutmacher D, Swieszkowski W, Moskalewski S.Insight into characteristic features of cartilage growth plate as a physiological template for bone formation. J Biomed Mater Res A 2016;104:357–366. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

