Synthetic alternatives to Matrigel
- PMID: 32953138
- PMCID: PMC7500703
- DOI: 10.1038/s41578-020-0199-8
Synthetic alternatives to Matrigel
Abstract
Matrigel, a basement-membrane matrix extracted from Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm mouse sarcomas, has been used for more than four decades for a myriad of cell culture applications. However, Matrigel is limited in its applicability to cellular biology, therapeutic cell manufacturing and drug discovery owing to its complex, ill-defined and variable composition. Variations in the mechanical and biochemical properties within a single batch of Matrigel - and between batches - have led to uncertainty in cell culture experiments and a lack of reproducibility. Moreover, Matrigel is not conducive to physical or biochemical manipulation, making it difficult to fine-tune the matrix to promote intended cell behaviours and achieve specific biological outcomes. Recent advances in synthetic scaffolds have led to the development of xenogenic-free, chemically defined, highly tunable and reproducible alternatives. In this Review, we assess the applications of Matrigel in cell culture, regenerative medicine and organoid assembly, detailing the limitations of Matrigel and highlighting synthetic scaffold alternatives that have shown equivalent or superior results. Additionally, we discuss the hurdles that are limiting a full transition from Matrigel to synthetic scaffolds and provide a brief perspective on the future directions of synthetic scaffolds for cell culture applications.
Figures
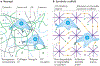

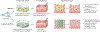

References
-
- LeBleu VS, Macdonald B & Kalluri R Structure and function of basement membranes. Exp. Biol. Med 232, 1121–1129 (2007). - PubMed
-
-
Kleinman HK et al. Basement membrane complexes with biological activity. Biochemistry 25, 312–318 (1986).
This paper investigates the protein composition and biological activity of the basement membrane extract from EHS mouse chondrosarcomas; this extract was later developed and commercialized as Matrigel.
-
-
- Kleinman HK & Martin GR Matrigel: basement membrane matrix with biological activity. Semin. Cancer Biol 15, 378–386 (2005). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
