Impact of examined lymph node count on prognosis in patients with lymph node-negative pancreatic body/tail ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 32953148
- PMCID: PMC7475334
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-20-158
Impact of examined lymph node count on prognosis in patients with lymph node-negative pancreatic body/tail ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Because the overall prognosis remains dismal for patients with resected pancreatic cancer (PC), we aimed to explore the prognostic impact of examined lymph node (ELN) count on lymph node (LN)-negative pancreatic body/tail ductal adenocarcinoma.
Methods: Patients' data were extracted from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database (National Cancer Institute, USA) to investigate the relationship between ELN count and survival outcomes of LN-negative pancreatic body/tail ductal adenocarcinoma.
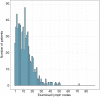
Results: A total of 700 patients were included, and the median number of ELNs was 11. The respective 1-, 3-, 5-year overall survival (OS) rates were 75.3%, 37.7%, 30.3%, and the 1-, 3-, 5-year cancer-specific survival (CSS) were 78.3%, 41.7%, 34.5%. The X-tile analysis showed that 14 was the most optimal cutoff for both OS and CSS. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis indicated that patients with ELNs >14 had better OS and CSS than ELNs ≤14. Multivariate Cox analysis showed ELNs ≤14 was an independent risk factor for both OS [hazard ratio (HR), 1.357; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.080-1.704; P=0.009] and CSS (HR, 1.394; 95% CI, 1.092-1.778; P=0.008).
Conclusions: ELN count is associated with the survival rate in patients with LN-negative pancreatic body/tail ductal adenocarcinoma. Accurate nodal staging for these patients requires more than 14 ELNs.
Keywords: Lymph nodes (LNs); Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (SEER database); pancreatic cancer (PC); prognosis.
2020 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jgo-20-158). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impact of examined lymph node count on staging and long-term survival of patients with node-negative stage III gastric cancer: a retrospective study using a Chinese multi-institutional registry with Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data validation.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Sep;8(17):1075. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-1358a. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33145294 Free PMC article.
-
The assessment of the optimal number of examined lymph nodes and prognostic models based on lymph nodes for predicting survival outcome in patients with stage N3b gastric cancer.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2021 Apr;17(2):e117-e124. doi: 10.1111/ajco.13358. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32762113
-
The impact of examined lymph node count on survival in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix.Cancer Manag Res. 2017 Jul 18;9:315-322. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S141335. eCollection 2017. Cancer Manag Res. 2017. PMID: 28761376 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of examined lymph node number on lymph node status and prognosis in FIGO stage IB-IIA cervical squamous cell carcinoma: A population-based study.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 20;12:994105. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.994105. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36203444 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Non-Peripancreatic Lymph Nodes in the Survival of Patients Suffering from Pancreatic Cancer of the Body and Tail: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of High-Quality Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 16;15(8):2322. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082322. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Survival Outcomes in Nonmetastatic pT4 Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A SEER Database Analysis Comparing Neoadjuvant Therapy and Upfront Surgery with Propensity Score Matching.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025 Mar 1;26(3):847-859. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.3.847. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 40156401 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
