Comparison of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with raltitrexed plus liposomal doxorubicin vs. tegafur plus pirarubicin for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 32953158
- PMCID: PMC7475337
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-20-59
Comparison of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with raltitrexed plus liposomal doxorubicin vs. tegafur plus pirarubicin for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: There is still no general consensus on the optimal chemotherapeutic agent selection for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The present study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of TACE with raltitrexed plus liposomal doxorubicin (R + PGLD) vs. tegafur plus pirarubicin (T + P) in patients with unresectable HCC.
Methods: A total of 148 patients with unresectable HCC treated with TACE between January 2012 and December 2016 were retrospectively analyzed. Of them, 74 patients were in the R + PGLD group and 74 patients were in the T + P group (1:1). The treatment response of the tumor, overall survival (OS) time, and adverse effects were compared between the two groups.
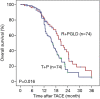
Results: There were no significant differences in patient characteristics or embolization effect (lipiodol deposition) between the two groups (P>0.05). R + PGLD treatment had a better clinical efficacy than T + P treatment (OR: 64.9% vs. 45.9%, P=0.031; DC: 89.2% vs. 74.3%, P=0.032). Portal vein invasion, hepatic vein invasion, tumor size and BCLC stage were associated with OR or DC after TACE using R + PGLD treatment. Survival analysis revealed that patients who received TACE with R + PGLD had a better prognosis than those treated with T + P. Moreover, some complications in the R + PGLD group, including vomiting, myelosuppression and cardiotoxicity, were significantly lower than those in the T + P group (P<0.05).
Conclusions: TACE with raltitrexed and liposomal doxorubicin could reduce the incidence of adverse reactions and significantly improve the OS of patients with unresectable HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); liposomal doxorubicin; prognosis; raltitrexed; transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE).
2020 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jgo-20-59). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of raltitrexed-based transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter real-world study.Hepatol Res. 2021 Nov;51(11):1153-1163. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13708. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Hepatol Res. 2021. PMID: 34492152
-
Transarterial chemoembolization with raltitrexed-based or floxuridine-based chemotherapy for unresectable colorectal cancer liver metastasis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 Apr;21(4):443-450. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1942-0. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30306400
-
Conversion Therapy of Large Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Ipsilateral Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus Using Portal Vein Embolization Plus Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 23;12:923566. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.923566. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35814420 Free PMC article.
-
Individual or combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a time-to-event meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Mar 19;19(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02188-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33741001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status and recent progress of nanomaterials in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Clin Oncol. 2025 Apr 24;16(4):104435. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104435. World J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40290691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multifunctional nanoplatforms application in the transcatheter chemoembolization against hepatocellular carcinoma.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Feb 27;21(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01820-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 36849981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial extracellular vesicles-based therapeutic strategies for bone and soft tissue tumors therapy.Theranostics. 2022 Sep 11;12(15):6576-6594. doi: 10.7150/thno.78034. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36185613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer Nanopharmaceuticals: Physicochemical Characterization and In Vitro/In Vivo Applications.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 15;13(8):1896. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081896. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Molecular Biology and Therapeutic Strategy Status and Prospects for circRNAs in HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 2;11:697747. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.697747. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34277444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of HBx carcinogenesis interaction with non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 8;13:1249198. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1249198. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37746253 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous