Caveolae-Mediated Transport at the Injured Blood-Brain Barrier as an Underexplored Pathway for Central Nervous System Drug Delivery
- PMID: 32953427
- PMCID: PMC7497790
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coche.2020.08.009
Caveolae-Mediated Transport at the Injured Blood-Brain Barrier as an Underexplored Pathway for Central Nervous System Drug Delivery
Abstract
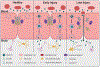
Drug delivery to the central nervous system (CNS) is generally hindered by the selectivity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). However, there is strong evidence that the integrity of the BBB is compromised under certain pathological conditions, potentially providing a window to deliver drugs to injured brain regions. Recent studies suggest that caveolae-mediated transcytosis, a transport pathway suppressed in the healthy BBB, becomes elevated as an immediate response to ischemic stroke and at early stages of aging, where it may precede irreversible neurological damage. This article reviews early-stage caveolar transcytosis as a novel and promising drug delivery opportunity. We propose that albumin-binding and nanoparticle approaches have the potential to leverage this window of transcellular BBB disruption for trafficking therapeutic agents into the CNS.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Andreone BJ, Chow BW, Tata A, Lacoste B, Ben-Zvi A, Bullock K, Deik AA, Ginty DD, Clish CB, Gu C, Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Is Regulated by Lipid Transport-Dependent Suppression of Caveolae-Mediated Transcytosis, Neuron. 94 (2017) 581–594.e5. 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.03.043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knowland D, Arac A, Sekiguchi KJ, Hsu M, Lutz SE, Perrino J, Steinberg GK, Barres BA, Nimmerjahn A, Agalliu D, Stepwise Recruitment of Transcellular and Paracellular Pathways Underlies Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Stroke, Neuron. 82 (2014) 603–617. 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.03.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
