Amyloid-ß peptides inhibit the expression of AQP4 and glutamate transporter EAAC1 in insulin-treated C6 glioma cells
- PMID: 32953460
- PMCID: PMC7484518
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.08.032
Amyloid-ß peptides inhibit the expression of AQP4 and glutamate transporter EAAC1 in insulin-treated C6 glioma cells
Abstract
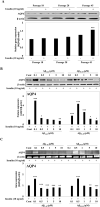
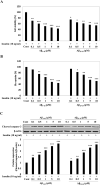
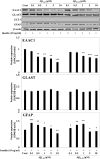
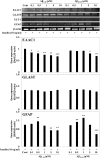
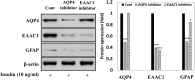
Astrocytic aquaporin 4 (AQP4) facilitates glutamate clearance via regulation of the glutamate transporter function, involved in the modulation of brain plasticity and cognitive function to prevent neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). In in vitro studies, the C6 rat glioma cell line is a widely applied aging model system to investigate changes in glial cells associated with aging or AD. However, the neurotoxicity mechanism whether AQP4 mediate glutamate uptake in Aβ-stimulated C6 cell remain uncertain. In this study, we examined the effects of Aβ on the expression of AQP4, Glu transporters, Glu uptake, and cell viability in insulin-treated C6 cells. Our results showed that the expression of AQP4 mRNA and protein was significantly enhanced by insulin in older cultures (passage 45), and the expression was inhibited by Aβ at 10 μM. In addition, the cell viability and glutamate uptake in Aβ-treated C6 cells were decreased in dose-dependent manners. GFAP showed similar changes in gene and protein expression patterns as AQP4, but no significant alterations were seen in GLAST expression. In C6 cells, the glutamate transport was found to be EAAC1, not GLT-1. EAAC1 expression was decreased by the treatment of Aβ. Taken together, our findings suggest that C6 cells may have astrocytic characteristics, and the astrocytic cytotoxicity induced by Aβ was mediated by reduction of glutamate uptake through AQP4/EAAC1 pathway in C6 cells. This indicates that C6 glioma cells could be used to study the roles of AQP4 on astrocyte function in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid β; Aquaporin 4; Glutamate transporter excitatory amino acid carrier 1; Glutamate uptake.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Na+-dependent glutamate transport activity in synaptosomes, C6 glioma, and Xenopus oocytes expressing excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1).Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Mar;49(3):465-73. Mol Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8643086
-
Altered expression of glutamate transporter-1 and water channel protein aquaporin-4 in human temporal cortex with Alzheimer's disease.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;44(6):628-638. doi: 10.1111/nan.12475. Epub 2018 Mar 4. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29405337
-
Amyloid-beta peptide decreases glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes: involvement of oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades.Neuroscience. 2008 Oct 28;156(4):898-910. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.08.022. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18790019
-
The Potential Roles of Aquaporin 4 in Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;53(8):5300-9. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9446-1. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26433375 Review.
-
Aquaporin-4 and Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016 Mar 25;52(2):391-402. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150949. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 27031475 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered Clock Gene Expression in Female APP/PS1 Mice and Aquaporin-Dependent Amyloid Accumulation in the Retina.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 27;24(21):15679. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115679. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958666 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of hippocampal neuronal circuit function depends upon behavioral state in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 5;12(1):21022. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25364-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36471155 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of cellular effects of thymoquinone on glioma cell.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Jan 4;8:162-170. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.12.026. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33489775 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of anoxia-induced bioenergetic disturbance in astrocytes by methanol fruit extract of Tetrapleura tetraptera and in silico evaluation of the effect of its antioxidative constituents on excitotoxicity.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Jan 26;8:264-276. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.01.015. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33552925 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Astrocytic Dysfunction via AQP4/LRP1 Pathway by Zizania latifolia and Tricin in C6 Cells Exposed to Amyloid β and High-Dose Insulin and in Mice Treated with Scopolamine.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 25;35:e2412026. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2412.12026. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40016145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heneka M.T., Carson M.J., Khoury J.El, Landreth G.E., Brosseron F., Feinstein D.L., Jacobs A.H., Wyss-Coray T., Vitorica J., Ransohoff R.M., Herrup K., Frautschy S.A., Finsen B., Brown G.C., Verkhratsky A., Yamanaka K., Koistinaho J., Latz E., Halle A., Petzold G.C., Town T., Morgan D., Shinohara M.L., Perry V.H., Holmes C., Bazan N.G., Brooks D.J., Hunot S., Joseph B., Deigendesch N., Garaschuk O., Boddeke E., Dinarello C.A., Breitner C., Cole G.M., Golenbock D.T., Kummer M.P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:388–405. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Serrano-Poze A., Muzikansky A., Gόmez-Isla T., Growdon J.H., Betensky R.A., Frosch M.P., Hyman B.T. Differential relationships of reactive astrocytes and microglia to fibrillar amyloid deposits in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013;72:462–471. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182933788. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

