Dose-response relationship of stereotactic body radiotherapy for ultracentral tumor and comparison of efficacy with central tumor: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 32953504
- PMCID: PMC7481588
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-20-503
Dose-response relationship of stereotactic body radiotherapy for ultracentral tumor and comparison of efficacy with central tumor: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Ultracentral (UC) tumors, a subset of central lung tumors defined as those that abut the proximal bronchial tree (PBT), have been contraindicated for stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT). The present meta-analysis evaluated the efficacy of SBRT for UC and central tumors, and dose-response for local control (LC) of UC tumors.
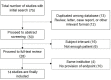
Methods: Databases including MEDLINE and EMBASE were searched up to March, 2020, to identify studies regarding SBRT for UC and/or central tumors. The primary endpoints were LC and overall survival (OS), while secondary endpoints were grade ≥3 and 5 complications.
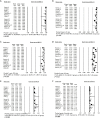
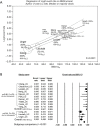
Results: Fourteen studies including 892 patients were included. In the UC and central tumor groups, the 1-year OS rates were 82.2% and 85.4% (P=0.556), respectively, and the 2-year OS rates were 66.4% and 71.9% (P=0.522), respectively. The 1- and 2-year LC rates in the UC and central tumor groups were 93.9% and 97.8% (P=0.023) and 90.4% and 93.7% (P=0.459), respectively. The pooled grade ≥3 complication rates in the UC and central tumor groups were 9.0% and 4.4% (P=0.06), while the corresponding grade 5 complication rates were 5.7% and 2.1% (P=0.087). The dose-response for LC was shown in the meta-regression (P<0.0001), and 1-year LC rates were significantly different (94.4% vs. 59.3%, P<0.001) with very low heterogeneities in both subgroups, with threshold of 85 Gy10. Of the 28 fatalities, 12 (42.8%) were caused by hemorrhage or bronchial stenosis, and another 12 (42.8%) by pneumonia or respiratory failure.
Conclusions: The oncologic outcomes of patients with UC and central tumors were comparable post-SBRT. A dose of at least ≥85 Gy10 is recommended for SBRT of UC tumors. Causes of complications should be further studied as UC tumors are more prone to serious toxicities.
Keywords: Lung cancer; central tumor; stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy; stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT); ultracentral (UC) tumor.
2020 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-20-503). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor Control and Toxicity after SBRT for Ultracentral, Central, and Paramediastinal Lung Tumors.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2019 Mar;9(2):e196-e202. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30496842 Free PMC article.
-
Is stereotactic body radiotherapy for ultra-central lung tumor a feasible option? A systemic review and meta-analysis.Int J Radiat Biol. 2019 Mar;95(3):329-337. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1552375. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019. PMID: 30676182
-
The safety and effectiveness of stereotactic body radiotherapy for central versus ultracentral lung tumors.Radiother Oncol. 2018 Nov;129(2):277-283. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Radiother Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30049454
-
Magnetic Resonance-Guided Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy/Hypofractionated Radiation therapy for Metastatic and Primary Central and Ultracentral Lung Lesions.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023 Feb 25;4(5):100488. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2023.100488. eCollection 2023 May. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023. PMID: 37159821 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic outcome and related predictors of stereotactic body radiotherapy for small liver-confined HCC: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Apr 8;16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01761-1. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33832536 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Stereotactic ablative body radiation therapy for treatment of ultra-central lung tumors: a narrative review.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Jun 30;17(6):4269-4286. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2024-1961. Epub 2025 Jun 26. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40688331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Moderate-Intensity Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Ultra-Central Lung Tumor.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Mar 26;60(4):538. doi: 10.3390/medicina60040538. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38674184 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric Analysis of Proximal Bronchial Tree Subsegments to Assess The Risk of Severe Toxicity After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy of Ultra-central Lung Tumors.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023 Dec 7;45:100707. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100707. eCollection 2024 Mar. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38125648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Cancer Comprehensive Network (NCCN). Principles of radiation therapy (NSCL-C), Non-small cell lung cancer. NCCN guidelines version 4.2019. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
