Radiomic features of primary tumor by lung cancer stage: analysis in BRAF mutated non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 32953516
- PMCID: PMC7481629
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-20-347
Radiomic features of primary tumor by lung cancer stage: analysis in BRAF mutated non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The clinical features and traditional semantic imaging characteristics of BRAF-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have been previously reported. The radiomic features of BRAF-mutated NSCLC and their role in predicting cancer stage, however, have yet to be investigated. This study's goal is to assess the differences in CT radiomic features of primary NSCLC driven by BRAF mutation and stratified by tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging.
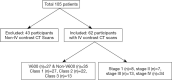
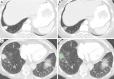
Methods: Our IRB approved study included 62 patients with BRAF mutations (V600 in 27 and non-V600 in 35 patients), who underwent contrast-enhanced chest CT. Tumor stage was determined based on the 8th edition of TNM staging. Two thoracic radiologists assessed the primary tumor imaging features such, including tumor size (maximum and minimum dimensions) and density (Hounsfield units, HU). De-identified transverse CT images (DICOM) were processed with 3D slicer (Version 4.7) for manual lesion segmentation and estimation of radiomic features. Descriptive statistics, multivariate logistic regression, and receiver operating characteristics (ROC) were performed.
Results: There were significant differences in the radiomic features based on cancer stages I-IV with the most significant differences between stage IV and stage I lesions [AUC 0.94 (95% CI: 0.86-0.99), P<0.04]. There were also significant differences in radiomic features between stage IV and combined stages I-III [40/113 radiomic features; AUC 0.71 (95% CI: 0.59-0.85); P<0.04-0.0001]. None of the clinical (0/6) or imaging (0/3) features were significantly different between stage IV and combined stages I-III.
Conclusions: The radiomic features of primary tumor in BRAF driven NSCLC significantly vary with cancer stage, independent of standard imaging and clinical features.
Keywords: BRAF; lung cancer; multidetector row computed tomography; radiomics.
2020 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-20-347). Dr. IDJ reports personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, and AstraZeneca, personal fees from Foundation Medicine, personal fees from Array and Pfizer, grants from Array, Genentech, Pfizer, and Guardant Health, outside the submitted work; Dr. MKK reports grants from Riverain technologies, grants from Siemens Healthineers, outside the submitted work. Dr. SRD reports Merck, Pfizer, Bristol Mayer Squibb, Novartis, Roche, Polaris, Cascadian, Abbvie, Gradalis, Clinical Bay, Zai laboratories, Siemens Medical Solutions, Lunit INC, outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Applicability of a prognostic CT-based radiomic signature model trained on stage I-III non-small cell lung cancer in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2018 Oct;124:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.07.023. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30268481 Clinical Trial.
-
Predicting malignant potential of subsolid nodules: can radiomics preempt longitudinal follow up CT?Cancer Imaging. 2019 Jun 10;19(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40644-019-0223-7. Cancer Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31182167 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Nomogram Combining CT Imaging with Clinical Features for Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Stage I-IIIB Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022 Jan;56(1):155-167. doi: 10.1007/s43441-021-00345-1. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022. PMID: 34699046
-
Prediction of pathological nodal involvement by CT-based Radiomic features of the primary tumor in patients with clinically node-negative peripheral lung adenocarcinomas.Med Phys. 2018 Jun;45(6):2518-2526. doi: 10.1002/mp.12901. Epub 2018 Apr 29. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29624702 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting survival time of lung cancer patients using radiomic analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 1;8(61):104393-104407. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22251. eCollection 2017 Nov 28. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29262648 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between tumor size and peritumoral brain edema in patients with convexity and parasagittal meningiomas.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 10;16(6):e0252945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252945. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34111188 Free PMC article.
-
Intelligent prognosis evaluation system for stage I-III resected non-small-cell lung cancer patients on CT images: a multi-center study.EClinicalMedicine. 2023 Oct 24;65:102270. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102270. eCollection 2023 Nov. EClinicalMedicine. 2023. PMID: 38106558 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics prediction of surgery in ulcerative colitis refractory to medical treatment.Tech Coloproctol. 2025 May 10;29(1):113. doi: 10.1007/s10151-025-03139-x. Tech Coloproctol. 2025. PMID: 40347388 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional radiomics for lung cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Nov;48(12):3961-3974. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05242-1. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33693966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feature selection methods and predictive models in CT lung cancer radiomics.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023 Jan;24(1):e13869. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13869. Epub 2022 Dec 17. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36527376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rami-Porta R, Bolejack V, Crowley J, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the Revisions of the T Descriptors in the Forthcoming Eighth Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2015;10:990-1003. - PubMed
-
- Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Travis WD, et al. Lung cancer - major changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin 2017;67:138-55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
