STAT1-p53-p21axis-dependent stress-induced progression of chronic nephrosis in adriamycin-induced mouse model
- PMID: 32953802
- PMCID: PMC7475511
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-5167
STAT1-p53-p21axis-dependent stress-induced progression of chronic nephrosis in adriamycin-induced mouse model
Erratum in
-
Erratum to STAT1-p53-p21axis-dependent stress-induced progression of chronic nephrosis in adriamycin-induced mouse model.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Oct;9(19):1512. doi: 10.21037/atm-2021-27. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34805374 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Chronic nephrosis (CN) is an aging-related disease with high mortality. Signal transduction and transcriptional activator 1 (STAT1) protein promotes senescence in human glomerular mesangial cells (HMCs), but whether it affects the progression of adriamycin (ADR)-induced CN in vivo remains unclear.
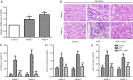
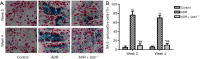
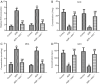
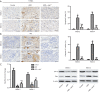
Methods: We established an ADR-induced CN mouse model that was completed in wild-type (wt) mice by a single intravenous injection of 10 mg/kg ADR for 2 or 4 weeks. Clinical indexes in each group were determined. Hematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E) was employed to determine renal histopathological damage, SA-β-gal staining was used to evaluate cell senescence phenotype. TUNEL and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining were used to detect renal apoptosis. Protein levels of Bcl-2, Bax, STAT1, p53 and p21 were measured by Western Blot.
Results: STAT1 intervention ameliorated renal function. H&E staining indicated that STAT1-deficient (stat1-/- ) improved the renal tubular injury, and stat1-/- obviously inhibited the apoptosis and Caspase-3+ number in kidney tissues. Besides, stat1-/- decreased proteinuria, and the levels of urea nitrogen and creatinine as well as that of reactive oxygen species induced by ADR. Also, stat1-/- resulted in the reduced expression of p53 and p21.
Conclusions: Our current study strongly demonstrated the involvement of the STAT1-p53-p21 axis in the regulation of CN and is a potential target for the nephrosis treatment.
Keywords: Adriamycin; STAT1; chronic nephrosis (CN); mitogen-activated protein kinase; senescence.
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-5167). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
STAT1 mediates cellular senescence induced by angiotensin II and H₂O₂ in human glomerular mesangial cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;365(1-2):9-17. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1197-3. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22193460
-
Losartan inhibits STAT1 activation and protects human glomerular mesangial cells from angiotensin II induced premature senescence.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;90(1):89-98. doi: 10.1139/y11-105. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22217266
-
[Slowing the progression of chronic renal insufficiency with captopril in rats with spontaneous arterial hypertension and adriamycin nephropathy].Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2002 Mar-Apr;130(3-4):73-80. doi: 10.2298/sarh0204073j. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2002. PMID: 12154518 Serbian.
-
[Relationship between glomerular nephrin expression and oxidative stress reaction in rats with adriamycin-induced nephrosis].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Jan;11(1):56-60. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19149925 Chinese.
-
Tripterygium glycoside fraction n2 ameliorates adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrome in rats by suppressing apoptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Jul 15;257:112789. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112789. Epub 2020 Mar 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32234597
Cited by
-
T-2 toxin-induced splenic injury by disrupting the gut microbiota-spleen axis via promoting IL-6/JAK/STAT1 signaling-mediated inflammation and apoptosis and its mitigation by elemental nano-selenium.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jun;99(6):2655-2667. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-04005-3. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40014112
-
Impact of Cigarette Smoking on the Expression of Oxidative Stress-Related Genes in Cumulus Cells Retrieved from Healthy Women Undergoing IVF.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 5;22(23):13147. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313147. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884952 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum to STAT1-p53-p21axis-dependent stress-induced progression of chronic nephrosis in adriamycin-induced mouse model.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Oct;9(19):1512. doi: 10.21037/atm-2021-27. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34805374 Free PMC article.
-
JAK Inhibition Prevents DNA Damage and Apoptosis in Testicular Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Modulation of the ATM/ATR/Chk Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 13;22(24):13390. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413390. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948185 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
