Circulating miR-216a as a biomarker of metabolic alterations and obesity in women
- PMID: 32954093
- PMCID: PMC7479169
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2020.08.001
Circulating miR-216a as a biomarker of metabolic alterations and obesity in women
Abstract
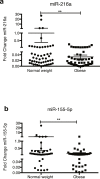
Obesity leads to an amplified risk of disease and contributes to the occurrence of type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease, coronary heart disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease and various types of cancer. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), small non-coding RNA molecules of 20-25 nucleotides, can remain stable in plasma and have been studied as potential (predictive) biomarkers for obesity and related metabolic disorders. The aim of this study was to identify circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for obesity status and metabolic alterations in women. Circulating miR-216a and miR-155-5p were selected by miRNA expression profiling and validated by real time quantitative PCR in a validation cohort of 60 obese women and 60 normal weight-age-matched control women. This was supplemented by correlation analysis of the candidate miRNA and anthropometric variables, blood biochemistry and lipid profile markers. Circulating miR-216a was validated as a biomarker of obesity status with significantly reduced levels in obese women. Interestingly, this was associated with a negative correlation between the plasma miR-216a content and body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, mean arterial pressure (MAP), triglycerides, ratio of total cholesterol/high density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol and high sensitivity-C reactive protein (hs-CRP).Taken together, we provide evidence for an abnormally expressed circulating miRNA, miR-216a, with additive value as a predictive marker for obesity that correlates with metabolic alterations presented by lipid profile and inflammatory markers.
Keywords: Biomarker; Metabolic syndrome; Obesity; microRNA.
© 2020 [The Author/The Authors].
Conflict of interest statement
P.D.C.M and L.D.W are co-founders and stockholders of Mirabilis Therapeutics BV. TT is founder and shareholder of Cardior Pharmaceuticals GmbH. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hu G. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and its relation to all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in nondiabetic European men and women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004;164(10):1066–1076. - PubMed
-
- D'Agati V.D. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: clinical and pathologic characteristics and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016;12(8):453–471. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

