Ramucirumab or placebo plus erlotinib in EGFR-mutated, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: East Asian subset of RELAY
- PMID: 32954593
- PMCID: PMC7734014
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.14655
Ramucirumab or placebo plus erlotinib in EGFR-mutated, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: East Asian subset of RELAY
Erratum in
-
Correction.Cancer Sci. 2021 May;112(5):2064. doi: 10.1111/cas.14922. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33934431 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
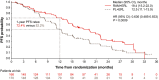
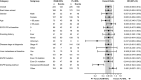
In the global phase III RELAY study, ramucirumab plus erlotinib (RAM + ERL) demonstrated superior progression-free survival (PFS) to placebo plus erlotinib (PL + ERL) in untreated patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (hazard ratio (HR) [95% CI]: 0.59 [0.46-0.76]). This prespecified analysis assessed RAM + ERL efficacy and safety in the RELAY subset enrolled in East Asia (Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, Hong Kong). Randomized (1:1) patients received oral ERL (150 mg/d) plus intravenous RAM (10 mg/kg) or PL Q2W. Primary endpoint was PFS (investigator-assessed). Key secondary endpoints included objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), duration of response (DoR), overall survival (OS), and safety. Exploratory endpoints included biomarker analyses and time to second progression (PFS2). Median PFS was 19.4 vs 12.5 mo for RAM + ERL (n = 166) vs PL + ERL (n = 170) (HR: 0.636 [0.485-0.833]; P = .0009). The 1-y PFS rate was 72.4% vs 52.2%, respectively. PFS benefit was consistent in most subgroups, including by EGFR mutation (Ex19del, Ex21.L858R). ORR and DCR were similar in both arms, but median DoR was longer with RAM + ERL. OS and PFS2 were immature at data cut-off (censoring rates, 81.2%-84.3% and 64.1%-70.5%, respectively). Grade ≥ 3 treatment-emergent adverse events were more frequent with RAM + ERL (70.7%) than PL + ERL (49.4%). Adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation were similar in both arms (RAM + ERL, 13.3%; PL + ERL, 12.9%), as were post-progression EGFR T790M mutation rates (43%; 50%). With superior PFS over PL + ERL and safety consistent with the overall RELAY population, RAM + ERL is a viable treatment option for EGFR-mutated metastatic NSCLC in East Asia.
Keywords: East Asia; epidermal growth factor receptor; erlotinib hydrochloride; non-small-cell lung cancer; ramucirumab.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Nishio has received lecture fees, honoraria, or other fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo Healthcare, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, and Taiho Pharmaceutical, and research funds from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, and Taiho Pharmaceutical. T. Seto is an employee of Precision Medicine Asia and has received lecture fees, honoraria, or other fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly Japan, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer Japan, and Taiho Pharmaceutical, and research funds from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly Japan, Kissei Pharmaceutical, LOXO Oncology, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer Japan, and Takeda Pharmaceutical. M. Reck has no conflicts of interest to declare. E. B. Garon has received lecture fees, honoraria, or other fees from Novartis, and research funds from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, EMD Serono, Genentech, Iovance, Merck, Mirati, Neon, and Novartis. C.‐H. Chiu has no conflicts of interest to declare. K. Yoh has received lecture fees, honoraria, or other fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical and Eli Lilly and Company, and research funds from Eli Lilly and Company. F. Imamura has received lecture fees, honoraria, or other fees from AstraZeneca, and research funds from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Chugai Pharmaceutical. K. Park has no conflicts of interest to declare. J.‐Y. Shih has no conflicts of interest to declare. C. Visseren‐Grul, B. Frimodt‐Moller, A. Zimmermann, G. Homma, and S. Enatsu are employees and minor shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company. K. Nakagawa has received lecture fees, honoraria, or other fees from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly Japan, Kyorin Pharmaceutical, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, and Pfizer Japan, and research funds from A2 Healthcare Corporation, AbbVie, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharmaceutical, CMIC Shift Zero, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly Japan, ICON Japan, inVentiv Health Japan, IQVIA Services Japan, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Ono Pharmaceutical, Pfizer Japan, SymBio Pharmaceuticals Limited, Syneos Health, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Taiho Pharmaceutical.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . GLOBOCAN 2018. Cancer Fact Sheets: Eastern Asia. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2018. http://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/906‐eastern‐asia‐fa.... Accessed December 10, 2019.
-
- Hsu WH, Yang JCH, Mok TS, Loong HH. Overview of current systemic management of EGFR‐mutant NSCLC. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:i3‐i9. - PubMed
-
- Hanna N, Johnson D, Temin S, et al. Systemic therapy for stage IV non‐small‐cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3484‐3515. - PubMed
-
- Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K, et al. Metastatic non‐small cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:863‐870. - PubMed
-
- Graham RP, Treece AL, Lindeman NI, et al. Worldwide frequency of commonly detected EGFR mutations. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142:163‐167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

