Apelin signaling drives vascular endothelial cells toward a pro-angiogenic state
- PMID: 32955436
- PMCID: PMC7567607
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.55589
Apelin signaling drives vascular endothelial cells toward a pro-angiogenic state
Abstract
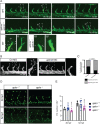
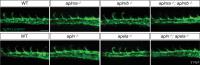
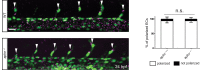
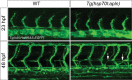
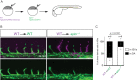
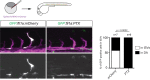
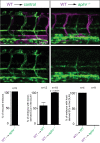
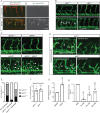
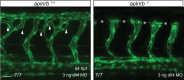
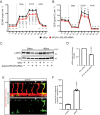
To form new blood vessels (angiogenesis), endothelial cells (ECs) must be activated and acquire highly migratory and proliferative phenotypes. However, the molecular mechanisms that govern these processes are incompletely understood. Here, we show that Apelin signaling functions to drive ECs into such an angiogenic state. Zebrafish lacking Apelin signaling exhibit defects in endothelial tip cell morphology and sprouting. Using transplantation experiments, we find that in mosaic vessels, wild-type ECs leave the dorsal aorta (DA) and form new vessels while neighboring ECs defective in Apelin signaling remain in the DA. Mechanistically, Apelin signaling enhances glycolytic activity in ECs at least in part by increasing levels of the growth-promoting transcription factor c-Myc. Moreover, APELIN expression is regulated by Notch signaling in human ECs, and its function is required for the hypersprouting phenotype in Delta-like 4 (Dll4) knockdown zebrafish embryos. These data provide new insights into fundamental principles of blood vessel formation and Apelin signaling, enabling a better understanding of vascular growth in health and disease.
Keywords: angiogenesis; apelin; developmental biology; endothelial cells; metabolism; notch; sprouting; zebrafish.
© 2020, Helker et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CH, JE, KW, TS, JM, AS, SB, HK, HM, MP, WH No competing interests declared, DS Senior editor, eLife
Figures
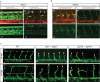
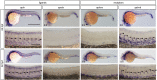
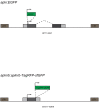
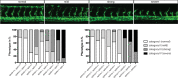
Similar articles
-
Essential role of Apelin signaling during lymphatic development in zebrafish.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Feb;34(2):338-45. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302785. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24311379 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish Tmem230a cooperates with the Delta/Notch signaling pathway to modulate endothelial cell number in angiogenic vessels.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Feb;233(2):1455-1467. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26032. Epub 2017 Jul 4. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28542953
-
E-Prostanoid 3 Receptor Mediates Sprouting Angiogenesis Through Suppression of the Protein Kinase A/β-Catenin/Notch Pathway.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 May;37(5):856-866. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308587. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28254818
-
Maturation of blood vessels by haematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells: involvement of apelin/APJ and angiopoietin/Tie2 interactions in vessel caliber size regulation.Thromb Haemost. 2009 Jun;101(6):999-1005. Thromb Haemost. 2009. PMID: 19492139 Review.
-
VEGFRs and Notch: a dynamic collaboration in vascular patterning.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Dec;37(Pt 6):1233-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0371233. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19909253 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Vascular Development in Zebrafish.Life (Basel). 2021 Oct 15;11(10):1088. doi: 10.3390/life11101088. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VCAM-1 Promotes Angiogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Patients with Trauma-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head by Regulating the Apelin/CCN2 Pathway.Stem Cells Int. 2023 Oct 12;2023:6684617. doi: 10.1155/2023/6684617. eCollection 2023. Stem Cells Int. 2023. PMID: 37868703 Free PMC article.
-
Key molecular alterations in endothelial cells in human glioblastoma uncovered through single-cell RNA sequencing.JCI Insight. 2021 Aug 9;6(15):e150861. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.150861. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34228647 Free PMC article.
-
APJ as Promising Therapeutic Target of Peptide Analogues in Myocardial Infarction- and Hypertension-Induced Heart Failure.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 4;15(5):1408. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051408. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircANKRD12 Is Induced in Endothelial Cell Response to Oxidative Stress.Cells. 2022 Nov 9;11(22):3546. doi: 10.3390/cells11223546. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36428974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alastalo TP, Li M, Perez VJ, Pham D, Sawada H, Wang JK, Koskenvuo M, Wang L, Freeman BA, Chang HY, Rabinovitch M. Disruption of PPARγ/β-catenin-mediated regulation of apelin impairs BMP-induced mouse and human pulmonary arterial EC survival. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2011;121:3735–3746. doi: 10.1172/JCI43382. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chandra SM, Razavi H, Kim J, Agrawal R, Kundu RK, de Jesus Perez V, Zamanian RT, Quertermous T, Chun HJ. Disruption of the apelin-APJ system worsens hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2011;31:814–820. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.219980. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

