A two-dimensional multiwell cell culture method for the production of CYP3A4-expressing hepatocyte-like cells from HepaRG cells
- PMID: 32955797
- PMCID: PMC7507088
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.652
A two-dimensional multiwell cell culture method for the production of CYP3A4-expressing hepatocyte-like cells from HepaRG cells
Abstract
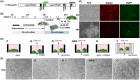
Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP) function in drug metabolism in the liver. To evaluate numerous drug candidates, a high-content screening (HCS) system with hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs) that can replace adult human hepatocytes is required. Human hepatocellular carcinoma HepaRG is the only cell line capable of providing HLCs with high CYP3A4 expression comparable to that in adult hepatocytes after cell differentiation. The aim of this study was to design an ideal multiwell culture system for HLCs using transgenic HepaRG cells expressing the EGFP coding an enhanced green fluorescent protein under CYP3A4 transcriptional regulation. HLCs were matured on five different types of 96-well black plates. Culturing HLCs on glass-bottom Optical CVG plates significantly promoted cell maturation and increased metabolic activity by twofold under two-dimensional (2D) culture conditions, and these features were enhanced by 2% collagen coating. Three plates for three-dimensional (3D) cell cultures with a gas-exchangeable fabric or dimethylpolysiloxane membrane bottom formed multiple round colonies, whereas they were ineffective for CYP3A4 expression. Under optimized conditions presented here, HLCs lost responsiveness to nuclear receptor-mediated transcriptional induction of CYP3A4, suggesting that CYP3A4 transcription has already been fully upregulated. Therefore, HepaRG-derived HLCs will provide an alternative to human hepatocytes with high levels of CYP3A4 enzyme activity even under 2D culture conditions. This will improve a variety of drug screening methods.
Keywords: CYP3A4; CYP3A7; HepaRG; a dual-color reporter; cytochrome P450 enzymes; hepatocyte-like cells; high-content screening.
© 2020 The Authors. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

