Selective inhibition of arginase-2 in endothelial cells but not proximal tubules reduces renal fibrosis
- PMID: 32956070
- PMCID: PMC7566719
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.142187
Selective inhibition of arginase-2 in endothelial cells but not proximal tubules reduces renal fibrosis
Abstract
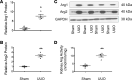
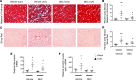
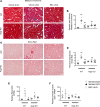
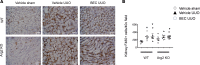
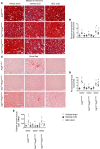
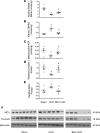
Fibrosis is the final common pathway in the pathophysiology of most forms of chronic kidney disease (CKD). As treatment of renal fibrosis still remains largely supportive, a refined understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of kidney fibrosis and the development of novel compounds are urgently needed. Whether arginases play a role in the development of fibrosis in CKD is unclear. We hypothesized that endothelial arginase-2 (Arg2) promotes the development of kidney fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Arg2 expression and arginase activity significantly increased following renal fibrosis. Pharmacologic blockade or genetic deficiency of Arg2 conferred kidney protection following renal fibrosis, as reflected by a reduction in kidney interstitial fibrosis and fibrotic markers. Selective deletion of Arg2 in endothelial cells (Tie2Cre/Arg2fl/fl) reduced the level of fibrosis after UUO. In contrast, selective deletion of Arg2 specifically in proximal tubular cells (Ggt1Cre/Arg2fl/fl) failed to reduce renal fibrosis after UUO. Furthermore, arginase inhibition restored kidney nitric oxide (NO) levels, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function following UUO. These findings indicate that endothelial Arg2 plays a major role in renal fibrosis via its action on NO and mitochondrial function. Blocking Arg2 activity or expression could be a novel therapeutic approach for prevention of CKD.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Mitochondria; Nephrology; Nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arginase-2 mediates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Aug 1;313(2):F522-F534. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00620.2016. Epub 2017 May 17. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. Retraction in: Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Oct 1;313(4):F1060. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.zh2-8358.retr-2017. PMID: 28515179 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Regulators of calcineurin 1 deficiency attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis through improving mitochondrial fitness.FASEB J. 2020 Nov;34(11). doi: 10.1096/fj.202000781RRR. Epub 2020 Sep 7. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32896034
-
PARK7 Protects Against Chronic Kidney Injury and Renal Fibrosis by Inducing SOD2 to Reduce Oxidative Stress.Front Immunol. 2021 May 21;12:690697. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.690697. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093596 Free PMC article.
-
Dual soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor/PPAR-γ agonist attenuates renal fibrosis.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020 Oct;150:106472. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2020.106472. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020. PMID: 32569747
-
Role of mitochondria in pathogenesis and therapy of renal fibrosis.Metabolism. 2024 Jun;155:155913. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2024.155913. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Metabolism. 2024. PMID: 38609039 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Targets of Brown Algae Phlorotannins for the Therapy of Inflammatory Processes of Various Origins.Mar Drugs. 2022 Mar 30;20(4):243. doi: 10.3390/md20040243. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35447916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Physiology to Pathology: The Role of Mitochondria in Acute Kidney Injuries and Chronic Kidney Diseases.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2023 Apr 4;9(5):342-357. doi: 10.1159/000530485. eCollection 2023 Oct. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37901706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PGC1α is required for the renoprotective effect of lncRNA Tug1 in vivo and links Tug1 with urea cycle metabolites.Cell Rep. 2021 Aug 10;36(6):109510. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109510. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34380028 Free PMC article.
-
Macula Densa Nitric Oxide Synthase 1β Restoration by Kidney Alkalization Enhances Renal Graft Outcomes.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Jul 21:10.1152/ajprenal.00195.2025. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00195.2025. Online ahead of print. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40691045 Free PMC article.
-
Aminoguanidine Prevents the Oxidative Stress, Inhibiting Elements of Inflammation, Endothelial Activation, Mesenchymal Markers, and Confers a Renoprotective Effect in Renal Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 28;10(11):1724. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111724. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829595 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

