A national consensus management pathway for paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19 (PIMS-TS): results of a national Delphi process
- PMID: 32956615
- PMCID: PMC7500943
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30304-7
A national consensus management pathway for paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19 (PIMS-TS): results of a national Delphi process
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Child Adolesc Health 2021; 5: 133-41.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021 Feb;5(2):e5. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30400-4. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021. PMID: 33484670 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
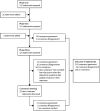
Paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19 (PIMS-TS) is a novel condition that was first reported in April, 2020. We aimed to develop a national consensus management pathway for the UK to provide guidance for clinicians caring for children with PIMS-TS. A three-phase online Delphi process and virtual consensus meeting sought consensus over the investigation, management, and research priorities from multidisciplinary clinicians caring for children with PIMS-TS. We used 140 consensus statements to derive a consensus management pathway that describes the initial investigation of children with suspected PIMS-TS, including blood markers to help determine the severity of disease, an echocardiogram, and a viral and septic screen to exclude other infectious causes of illness. The importance of a multidisciplinary team in decision making for children with PIMS-TS is highlighted throughout the guidance, along with the recommended treatment options, including supportive care, intravenous immunoglobulin, methylprednisolone, and biological therapies. These include IL-1 antagonists (eg, anakinra), IL-6 receptor blockers (eg, tocilizumab), and anti-TNF agents (eg, infliximab) for children with Kawasaki disease-like phenotype and non-specific presentations. Use of a rapid online Delphi process has made it possible to generate a national consensus pathway in a timely and cost-efficient manner in the middle of a global pandemic. The consensus statements represent the views of UK clinicians and are applicable to children in the UK suspected of having PIMS-TS. Future evidence will inform updates to this guidance, which in the interim provides a solid framework to support clinicians caring for children with PIMS-TS. This process has directly informed new PIMS-TS specific treatment groups as part of the adaptive UK RECOVERY trial protocol, which is the first formal randomised controlled trial of therapies for PIMS-TS globally.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Jones VG, Mills M, Suarez D, et al. COVID-19 and Kawasaki disease: novel virus and novel case. Hosp Pediatr. 2020;10:537–540. - PubMed
-
- Belhadjer Z, Méot M, Bajolle F, et al. Acute heart failure in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in the context of global SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Circulation. 2020;142:429–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous