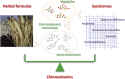
Chinmedomics, a new strategy for evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of herbal medicines
- PMID: 32956722
- PMCID: PMC7500400
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107680
Chinmedomics, a new strategy for evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of herbal medicines
Abstract
Herbal medicines have accumulated valuable clinical experience in thousands of years of applications in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) or ethnomedicine. The unique multi-target efficacy on complex diseases made herbal medicines gained a global popularity in recent years. However, the characteristic of multi-component acting on multi-target poses a dilemma for the evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of herbal medicines. Advances in metabolomics enable efficient identification of the various changes in biological systems exposed to different treatments or conditions. The use of serum pharmacochemistry of TCM has significant implications for tackling the major issue in herbal medicines development-pharmacodynamic material basis. Chinmedomics integrates metabolomics and serum pharmacochemistry of TCM to investigate the pharmacodynamic material basis and effective mechanisms of herbal medicines on the basis of TCM syndromes and holds the promise of explaining therapeutic efficacy of herbal medicines in scientific language. In this review, the historical development of chinmedomics from concept formation to successful applications was discussed. We also took the systematic research of Yin Chen Hao Tang (YCHT) as an example to show the research strategy of chinmedomics.
Keywords: Chinmedomics; Herbal medicines; Pharmacodynamic material basis; Quality control of herbal medicines; TCM syndrome.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Ying Han, Hui Sun, Aihua Zhang, Guangli Yan, and Xi-jun Wang declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bu Y., Hu Q., Xu K., Xie X., Wang S. Improved cell membrane bioaffinity sample pretreatment technique with enhanced stability for screening of potential allergenic components from traditional Chinese medicine injections. Journal of Materials Chemistry B. 2018;6:624–633. - PubMed
-
- Buyel J.F. Plants as sources of natural and recombinant anti-cancer agents. Biotechnology Advances. 2018;36:506–520. - PubMed
-
- Cao H., Zhang A., Zhang F.M., Wang Q.Q., Zhang H., Song Y.H., et al. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry combined with automated MetaboLynx analysis approach to screen the bioactive components and their metabolites in Wen-Xin-Formula. Biomedical Chromatography. 2014;28:1774–1781. - PubMed
-
- Chen C., Yang F.Q., Zuo H.L., Song Y.L., Xia Z.N., Xiao W. Applications of biochromatography in the screening of bioactive natural products. Journal of Chromatographic Science. 2013;51:780–790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources