Metabolite regulation of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter channel
- PMID: 32956979
- PMCID: PMC8017895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102288
Metabolite regulation of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter channel
Abstract
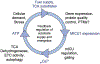
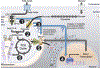
Calcium (Ca2+) is known to stimulate mitochondrial bioenergetics through the modulation of TCA cycle dehydrogenases and electron transport chain (ETC) complexes. This is hypothesized to be an essential pathway of energetic control to meet cellular ATP demand. While regulatory mechanisms of mitochondrial calcium uptake have been reported, it remains unknown if metabolite flux itself feedsback to regulate mitochondrial calcium (mCa2+) uptake. This hypothesis was recently tested by Nemani et al. (Sci. Signal. 2020) where the authors report that TCA cycle substrate flux regulates the mitochondrial calcium uniporter channel gatekeeper, mitochondrial calcium uptake 1 (MICU1), gene transcription in an early growth response protein 1 (EGR1) dependent fashion. They posit this is a regulatory feedback mechanism to control ionic homeostasis and mitochondrial bioenergetics with changing fuel availability. Here, we provide a historical overview of mitochondrial calcium exchange and comprehensive appraisal of these results in the context of recent literature and discuss possible regulatory pathways of mCa2+ uptake and mitochondrial bioenergetics.
Keywords: Calcium; Energetics; MCU; MICU1; MPC; Mitochondria; OXPHOS; TCA cycle; TCA substrates.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors reported no declarations of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Clapham DE, Calcium signaling, Cell 80 (1995) 259–268. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD, The versatility and universality of calcium signalling, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 1 (2000) 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki S, Shirakawa H, Nakada K, Honda Y, Essential role of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor/Ca2+ release channel in Ca2+ waves and Ca2+ oscillations at fertilization of mammalian eggs, Dev Biol 158 (1993) 62–78. - PubMed
-
- Kume S, Muto A, Inoue T, Suga K, Okano H, Mikoshiba K, Role of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in ventral signaling in Xenopus embryos, Science 278 (1997) 1940–1943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

