Arthroscopic treatment of adult displaced tibial eminence fractures with anchor and pushlock fixation
- PMID: 32957304
- PMCID: PMC7505351
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021237
Arthroscopic treatment of adult displaced tibial eminence fractures with anchor and pushlock fixation
Abstract
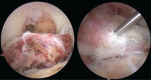
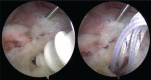
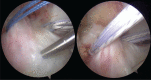
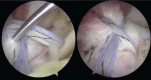
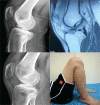
Arthroscopic techniques are considered the gold standard for treatment of displaced avulsion fractures of the anterior cruciate ligament. However, most arthroscopic surgical techniques and fixation methods are technically demanding and require removal of hard implant. This report describes a new, easy, safe, and all-arthroscopic method for reduction and fixation of displaced tibial intercondylar eminence fractures by using 1 anchor and 1 Pushlock.From January 2015 to June 2017, 8 adult patients with type II and III displaced tibial intercondylar eminence fractures were operated using this technique. Clinical assessment included patient demographics, cause of injury, delay before surgery, operation time, time to return to work and sport, International Knee Documentation Committee scores, and Lysholm knee scores.The average operation time was 48 minutes. The average follow-up period was 12.5 months. At the 6-month follow-up, all patients had acquired fracture union and complete functional recovery and were able to return to work. International Knee Documentation Committee objective scores and Lysholm knee scores were 92.4 (range 88-94) and 93.6 (range 90-96), respectively. At the last follow-up, anterior drawer, Lachman's test, and pivot shift tests were negative, and all patients had returned to their preinjury activity levels.Arthroscopic fixation by use of 1 anchor and 1 Pushlock is an easy, safe, and minimally invasive technique for treatment of displaced tibial intercondylar eminence fractures and does not require further surgery to remove fixation devices.Level of Evidence: Level IV, therapeutic case series.
Figures
References
-
- Kendall NS, Hsu SC, Chan KM. Facture of the tibial spine in adults and children. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1992;74:848–52.. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann KR, Edmonds EW. The pediatric ACL: tibial spine fracture. In: Parikh S, eds The Pediatric Anterior Cruciate Ligament Springer, Cham; 2018;211–22..
-
- Huang TW, Hsu KY, Cheng CY, et al. . Arthroscopic suture fixation of tibial eminence avulsion fractures. Arthroscopy 2008;24:1232–8.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

