Comparative efficacy and safety of different drugs for bipolar disorder complicated with anxiety disorder: A protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 32957382
- PMCID: PMC7505332
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022280
Comparative efficacy and safety of different drugs for bipolar disorder complicated with anxiety disorder: A protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Nowadays, there are some randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to explore the effectiveness of drug therapy for bipolar disorder with anxiety disorders. However, due to lack of sufficient data, there are currently no good treatment recommendations. The purpose of this network meta-analysis is to compare the efficacy and safety of different drugs for bipolar disorder complicated with anxiety disorders to provide evidence to support clinical practice and guidelines development.
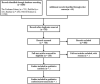
Methods: A systematic literature search will be performed in the Cochrane Library, PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science from inception to July 2020. RCTs that compared the efficacy and safety of different drugs for bipolar disorder complicated with anxiety disorders will be included. Two reviewers will independently search and select the studies, extract the data, and assess the risk of bias. We will assess the risk of bias of included RCTs using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. The WinBUGS 1.4.3 software will be used to perform the network meta-analysis, and the result figures will be generated by STATA 15.0 software. In addition, we will use the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) to assess the quality of evidence.
Results: This study will systematically compare the efficacy and safety of different drugs for bipolar disorder complicated with anxiety disorders. The results of this network meta-analysis will be submitted to a peer-reviewed journal for publication.
Conclusion: Our study will provide evidence for the drug therapy of patients with bipolar disorder complicated with anxiety disorders, and provide suggestions for clinical practice or guidelines.
Inplasy registration number: INPLASY202070132.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Effect of MBSR, DBT and CBT on the hypertension patients with depression/anxiety: Protocol of a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 21;18(2):e0281469. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281469. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36802399 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical antipsychotics for disruptive behaviour disorders in children and youths.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 9;8(8):CD008559. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008559.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28791693 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Atypical antipsychotics for disruptive behaviour disorders in children and youths.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;(9):CD008559. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008559.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 09;8:CD008559. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008559.pub3. PMID: 22972123 Updated.
Cited by
-
Untangling the complex relationship between bipolar disorder and anxiety: a comprehensive review of prevalence, prognosis, and therapy.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2025 Apr;132(4):567-578. doi: 10.1007/s00702-024-02876-x. Epub 2025 Jan 4. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2025. PMID: 39755917 Review.
References
-
- Fornaro M, Anastasia A, Novello S, et al. . Incidence, prevalence and clinical correlates of antidepressant-emergent mania in bipolar depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bipolar Disord 2018;20:195–227.. - PubMed
-
- Rakofsky JJ, Dunlop BW. Treating nonspecific anxiety and anxiety disorders in patients with bipolar disorder: a review. J Clin Psychiatry 2011;72:81–90.. - PubMed
-
- Tohen M, Calabrese J, Vieta E, et al. . Effect of comorbid anxiety on treatment response in bipolar depression. J Affect Disord 2007;104:137–46.. - PubMed