Investigation of Streptomyces scabies Causing Potato Scab by Various Detection Techniques, Its Pathogenicity and Determination of Host-Disease Resistance in Potato Germplasm
- PMID: 32957549
- PMCID: PMC7559370
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens9090760
Investigation of Streptomyces scabies Causing Potato Scab by Various Detection Techniques, Its Pathogenicity and Determination of Host-Disease Resistance in Potato Germplasm
Abstract
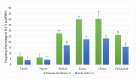
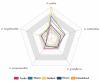
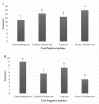
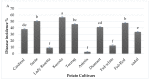
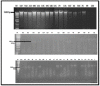
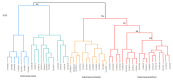
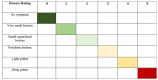
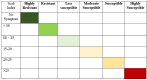
Streptomyces scabies is a Gram-positive bacterial pathogen that causes common scab disease to several crops, particularly in the potato. It is a soil borne pathogen, a very devastating scab pathogen and difficult to manage in the field. Streptomyces has several species that cause common scab such as S. scabiei, S. acidiscabies, S. europaeiscabiei, S. luridiscabiei, S. niveiscabiei, S. puniciscabiei, S. reticuliscabiei, S. stelliscabiei, S. turgidiscabies, S. ipomoeae. Common scab disease harmfully affects potato economic and market value due to the presence of black spots on the tuber. Owing to its genetic diversity and pathogenicity, the determination of pathogen presence in potato fields is still challenging. In this study, S. scabies genetic diversity was measured by surveying five potato-growing areas of Pakistan during the growing season 2019. A total of 50 Streptomyces isolates, including S. scabies, S. acidiscabies, S. griseoflavus were isolated and identified based on morphologic, biochemical and molecular analysis. Virulent confirmation assays confirmed ten virulent strains of Streptomyces spp. On the potato cultivars Cardinal and Santee. Among the Streptomyces species, S. scabies showed the highest scab index, followed by S. acidiscabies and S. griseoflavus by exhibiting the scab-like lesions on potato tubers. Ten potato cultivars were screened against these virulent isolates of Streptomyces. The Faisalabad white variety showed the highest scab index followed By Cardinal, Tourag, Kuroda, Santee, Lady Rosetta, Asterix, Diamant, Faisalabad red and Sadaf. Moreover, genetic diversity and pathogenicity of Streptomyces spp. on potato tubers were also likely diverse in different geographical regions and also potato cultivars. This study represents a contribution to understanding the local interaction between potatoes and Streptomyces spp. in Pakistan. It will aid in supporting a solution for the management of this pathogen around the world.
Keywords: Gram-positive bacteria; Streptomyces scabies; common scab disease; soil borne pathogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this work. All forms of financial support are acknowledged in the contribution. All authors have offered consent to submission.
Figures








References
-
- Majeed A., Muhammad Z. Potato production in Pakistan: Challenges and prospective management strategies–A review. Pak. J. Bot. 2018;50:2077–2084.
-
- Anwar D., Shabbir D., Shahid M.H., Samreen W. Determinants of Potato Prices and Its Forecasting: A Case Study of Punjab, Pakistan. [(accessed on 20 August 2020)];2015 Sep 16; Available online: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/66678/
-
- FAOSTAT . FAOSTAT Database Collections. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

