Prognostic Role and Clinical Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study
- PMID: 32957579
- PMCID: PMC7554852
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10090704
Prognostic Role and Clinical Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study
Abstract
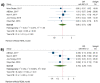
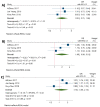
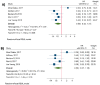
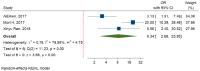
This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), their associations with the clinicopathological characteristics, and the association between their levels in patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, ProQuest, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases were searched to obtain the relevant papers. Seven studies with 1152 patients were included in this study. Like the level of TILs, there were no significant associations between PD-L1 expression and tumor size, tumor stage, lymph node metastasis, histological grade, and Ki67 (All p-values ≥ 0.05). Furthermore, there was no significant association between PD-L1 expression with overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS). In assessment of TILs and survival relationship, the results showed that a high level of TILs was associated with long-term OS (hazard ratios (HR) = 0.48, 95% CI: 0.30 to 0.77, p-value < 0.001) and DFS (HR = 0.53, 95% CI: 0.35 to 0.78, p-value < 0.001). The results displayed that tumoral PD-L1 expression was strongly associated with high levels of TILs in TNBC patients (OR = 8.34, 95% CI: 2.68 to 25.95, p-value < 0.001). In conclusion, the study has shown the prognostic value of TILs and a strong association between tumoral PD-L1 overexpression with TILs in TNBC patients.
Keywords: meta-analysis; prognosis; programmed cell death-ligand 1; triple-negative breast cancer; tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2020 Mar 4;20(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6668-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32131780 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic candidate for immune checkpoint inhibitors elucidated by the status of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC).Breast Cancer. 2018 Jan;25(1):34-42. doi: 10.1007/s12282-017-0781-0. Epub 2017 May 9. Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 28488168
-
Prognostic role and clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 May;25(5):1436-1445. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-03040-1. Epub 2022 Dec 18. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36528835
-
PD-L1 expression in tumor infiltrated lymphocytes predicts survival in triple-negative breast cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Mar;216(3):152802. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152802. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32005408
-
Prognostic Implications of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Association With Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Early-Stage Breast Cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2016 Feb;16(1):51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Clin Breast Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26364145
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review on PD-1 Blockade and PD-1 Gene-Editing of CAR-T Cells for Glioma Therapy: From Deciphering to Personalized Medicine.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 19;12:788211. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.788211. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35126356 Free PMC article.
-
Clinico-pathological relationship between androgen receptor and tumour infiltrating lymphocytes in triple negative breast cancer.Ecancermedicalscience. 2021 Nov 11;15:1317. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2021.1317. eCollection 2021. Ecancermedicalscience. 2021. PMID: 35047068 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Significance of TIGIT in Solid Cancers: Dual TIGIT/PD-1 Blockade to Overcome Immune-Resistance in Solid Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 27;22(19):10389. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910389. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638729 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Tumour-Infiltrating Lymphocytes for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Management.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2023 Nov 2;15:773-783. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S399157. eCollection 2023. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2023. PMID: 37936879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-infiltrating immune cells state-implications for various breast cancer subtypes.Front Immunol. 2025 May 14;16:1550003. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1550003. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40438111 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee J., Kim D.-M., Lee A. Prognostic Role and Clinical Association of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte, Programmed Death Ligand-1 Expression with Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Locally Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018;51:649–663. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.270. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li X., Yang J., Peng L., Sahin A.A., Huo L., Ward K.C., O’Regan R., Torres M.A., Meisel J.L. Triple-negative breast cancer has worse overall survival and cause-specific survival than non-triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016;161:279–287. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-4059-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

