The effectiveness of sedentary behaviour interventions on sitting time and screen time in children and adults: an umbrella review of systematic reviews
- PMID: 32958052
- PMCID: PMC7504841
- DOI: 10.1186/s12966-020-01009-3
The effectiveness of sedentary behaviour interventions on sitting time and screen time in children and adults: an umbrella review of systematic reviews
Abstract
Background: There is increasing concern about the time people spend in sedentary behaviour, including screen time, leisure and occupational sitting. The number of both primary research studies (published trials) and reviews has been growing rapidly in this research area. A summary of the highest level of evidence that provides a broader quantitative synthesis of diverse types of interventions is needed. This research is to articulate the evidence of efficacy of sedentary behaviour interventions to inform interventions to reduce sitting time. The umbrella review, therefore, synthesised systematic reviews that conducted meta-analyses of interventions aiming at reducing sedentary behaviour outcomes across all age group and settings.
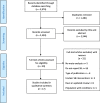
Method: A systematic search was conducted on six databases (MEDLINE Complete, PsycINFO, CINAHL, Global Health via EBSCOhost platform, EMBASE, and Cochrane Central Register of Systematic Reviews). Included articles were systematic reviews with meta-analysis of interventions aiming at reducing sedentary behaviour (screen time, sitting time or sedentary time) in the general population across all age group.
Results: Seventeen reviews met the inclusion criteria (7 in children and adolescent, 10 in adults). All reviews of sedentary behaviour interventions in children and adolescents investigated intervention effectiveness in reducing screen time. Six out of 11 meta-analyses (reported in 7 reviews) showed small but significant changes in viewing time. All reviews of sedentary behaviour interventions in office workplaces indicated substantial reduction in occupational sitting time (range: 39.6 to 100 min per 8-h workday). Sub-group analyses reported a trend favouring environmental change components such as sit-stand desks, active permissive workstations etc. Meta-analyses indicated that sedentary behaviour interventions were superior to physical activity alone interventions or combined physical activity and sedentary behaviour interventions in reducing sitting time.
Conclusion: The current systematic reviews and meta-analyses supported sedentary behaviour interventions for reducing occupational sitting time in particular, with small changes seen in screen time in children and adolescents. Future research should explore approaches to maintaining behaviour change beyond the intervention period and investigate the potential of sedentary behaviour reduction interventions in older age groups in non-occupational settings.
Keywords: Effectiveness; Screen time; Sedentary behaviour; Sedentary time; Sitting time; Systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous