Potent antiviral effect of silver nanoparticles on SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32958250
- PMCID: PMC7486059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.018
Potent antiviral effect of silver nanoparticles on SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
The pandemic of COVID-19 is spreading unchecked due to the lack of effective antiviral measures. Silver nanoparticles (AgNP) have been studied to possess antiviral properties and are presumed to inhibit SARS-CoV-2. Due to the need for an effective agent against SARS-CoV-2, we evaluated the antiviral effect of AgNPs. We evaluated a plethora of AgNPs of different sizes and concentration and observed that particles of diameter around 10 nm were effective in inhibiting extracellular SARS-CoV-2 at concentrations ranging between 1 and 10 ppm while cytotoxic effect was observed at concentrations of 20 ppm and above. Luciferase-based pseudovirus entry assay revealed that AgNPs potently inhibited viral entry step via disrupting viral integrity. These results indicate that AgNPs are highly potent microbicides against SARS-CoV-2 but should be used with caution due to their cytotoxic effects and their potential to derange environmental ecosystems when improperly disposed.
Keywords: COVID-19; Colloidal silver; SARS-CoV-2; Silver nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no conflicts of interest directly relevant to the content of this article. Y.Y. is a current employee of Kanto Chemical Co., Inc.
Figures

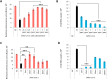
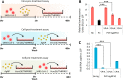
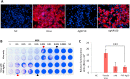
References
-
- Han J., Chen L., Duan S.-M., Yang Q.-X., Yang M., Gao C., Zhang B.-Y., He H., Dong X.-P. Efficient and quick inactivation of SARS coronavirus and other microbes exposed to the surfaces of some metal catalysts. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES. 2005;18:176–180. - PubMed
-
- Talebian S., Wallace G.G., Schroeder A., Stellacci F., Conde J. Nanotechnology-based disinfectants and sensors for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020;15:618–621. - PubMed
-
- Matsuyama S., Nao N., Shirato K., Kawase M., Saito S., Takayama I., Nagata N., Sekizuka T., Katoh H., Kato F., Sakata M., Tahara M., Kutsuna S., Ohmagari N., Kuroda M., Suzuki T., Kageyama T., Takeda M. Enhanced isolation of SARS-CoV-2 by TMPRSS2-expressing cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2020;117:7001–7003. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gordon D.E., Jang G.M., Bouhaddou M., Xu J., Obernier K., White K.M., O’Meara M.J., Rezelj V.V., Guo J.Z., Swaney D.L., Tummino T.A., Hüttenhain R., Kaake R.M., Richards A.L., Tutuncuoglu B., Foussard H., Batra J., Haas K., Modak M., Kim M., Haas P., Polacco B.J., Braberg H., Fabius J.M., Eckhardt M., Soucheray M., Bennett M.J., Cakir M., McGregor M.J., Li Q., Meyer B., Roesch F., Vallet T., Mac Kain A., Miorin L., Moreno E., Naing Z.Z.C., Zhou Y., Peng S., Shi Y., Zhang Z., Shen W., Kirby I.T., Melnyk J.E., Chorba J.S., Lou K., Dai S.A., Barrio-Hernandez I., Memon D., Hernandez-Armenta C., Lyu J., Mathy C.J.P., Perica T., Pilla K.B., Ganesan S.J., Saltzberg D.J., Rakesh R., Liu X., Rosenthal S.B., Calviello L., Venkataramanan S., Liboy-Lugo J., Lin Y., Huang X.-P., Liu Y., Wankowicz S.A., Bohn M., Safari M., Ugur F.S., Koh C., Savar N.S., Tran Q.D., Shengjuler D., Fletcher S.J., O’Neal M.C., Cai Y., Chang J.C.J., Broadhurst D.J., Klippsten S., Sharp P.P., Wenzell N.A., Kuzuoglu-Ozturk D., Wang H.-Y., Trenker R., Young J.M., Cavero D.A., Hiatt J., Roth T.L., Rathore U., Subramanian A., Noack J., Hubert M., Stroud R.M., Frankel A.D., Rosenberg O.S., Verba K.A., Agard D.A., Ott M., Emerman M., Jura N., von Zastrow M., Verdin E., Ashworth A., Schwartz O., d’Enfert C., Mukherjee S., Jacobson M., Malik H.S., Fujimori D.G., Ideker T., Craik C.S., Floor S.N., Fraser J.S., Gross J.D., Sali A., Roth B.L., Ruggero D., Taunton J., Kortemme T., Beltrao P., Vignuzzi M., García-Sastre A., Shokat K.M., Shoichet B.K., Krogan N.J. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature. 2020;583:459–468. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

